
Like all living creatures, these birds are susceptible to various diseases, which is one of the main challenges in poultry farming. Ideally, prevention is better than cure, and preventative measures should be taken to achieve this. However, sometimes even these measures are ineffective. Therefore, to successfully combat chicken diseases, both experienced and novice farmers must have a sufficient understanding of them.
This material covers the most common diseases, which can affect chicken flocks: clinical picture, modern diagnostic and treatment methods, as well as effective preventive measures.
Content
How to recognize if a chicken is sick?
In order to recognize the disease in time, you should regularly inspect your chicken flock and constantly monitor them.
While examining the bird, It is necessary to pay attention to:
feather cover (in healthy animals it is shiny and smooth)
- on the musculoskeletal system and coordination of movements (healthy chickens stand firmly on their feet and move confidently and without wobbling)
- on the digestive system (healthy birds have a good appetite, drink water and defecate regularly)
- for breathing (normally chickens breathe frequently and with their beaks closed; there should be no extraneous sounds when breathing: wheezing, groans, etc.)
If you do find pets that may have some kind of illness, isolate them from the rest and continue monitoring. Ideally, you should take the animal to a veterinarian.
The main groups of diseases that domestic chickens are susceptible to
Diseases affecting chickens are divided into two large groups: contagious (transmitted from bird to bird) and non-contagious (not transmitted).
Contagious include:
- infectious and fungal diseases,
- helminth infection,
- skin parasites.
Infectious diseases

The key to treating this condition is prompt diagnosis. Affected chickens are given aminoglycoside antibiotics (neomycin, biomycin) or penicillin (ampicillin) via water. These medications can also be administered intramuscularly.
To prevent the spread of pullorum, hygiene should be maintained in the chicken coop. If an outbreak of pullorum occurs, affected birds should be isolated and the coop disinfected.
Pseudoplague (Newcastle disease) — a viral infection transmitted by airborne droplets. Sources of infection include sick animals, their feed, and water. The disease affects the nervous and respiratory systems, as well as the gastrointestinal tract. Birds exhibit impaired coordination (unsteady gait, constantly falling on their stomachs), and mucus accumulates in the mouth. The chicken is forced to breathe with its beak open, and a distant wheezing sound can be heard when breathing. There is no appetite, and profuse diarrhea occurs.
This disease is incurable. Chickens exhibiting these symptoms must be immediately isolated, euthanized, and burned.
Failure to do so could result in the loss of the entire chicken flock. To prevent pseudoplague, it is necessary to promptly disinfect the chicken coop and vaccinate the birds.
Chicken pox - A viral disease that often affects domestic chickens. Its main symptom is the presence of skin ulcers (pox). Infection occurs by contact. The source may be:
- a sick laying hen or other pet,
- feed,
- water.
The virus targets the cornea and internal organs. Treatment is essential at the initial stage of the disease. External lesions are treated with antiseptics, such as boric acid solution or furacilin. Tetracycline is added to the feed for 7-10 days. If the disease is not detected at the initial stage, all infected birds must be culled.
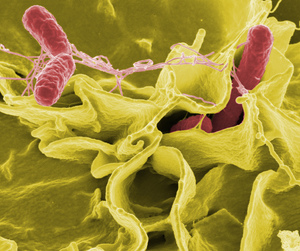
If domestic chickens are infected with salmonella, eating raw eggs is strictly prohibited, as they are the main source of salmonella infection in humans. These bacteria are killed only by prolonged heat treatment.
Treatment for this infectious disease lasts for 21 days. During this time, furazolidone is added to the chickens' water supply. Streptomycin can be administered with their feed. To prevent the spread of infection, infected birds should be isolated. The coop should be disinfected. To prevent salmonellosis, the birds should be vaccinated.
Tuberculosis — a bacterial infection transmitted by airborne droplets. It is caused by human and avian strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The disease occurs when birds are kept in unsanitary conditions. An infected hen is lethargic, drowsy, and has a pale comb. A key symptom is the absence of eggs. The animals experience rapid weight loss.
There is no cure for this infection, so sick animals must be culled. As a preventative measure, it is essential to keep the chicken coop clean at all times.

Treatment involves feeding the birds water containing potassium permanganate and administering antibiotics with tetracycline or fluoroquinolones. Chickens that have been in close contact with the birds but appear healthy should also be given antibiotics for two days as a preventative measure. The coop and all equipment must be disinfected.
Colinfection (colisepticemia) - A disease caused by a type of coliform bacteria. It occurs due to poor sanitary and hygienic conditions in the area where chickens are kept. Laying hens can also become infected through consuming poor-quality feed. Warning signs include lethargy and loss of appetite, accompanied by increasing thirst. Breathing becomes hoarse and labored. A characteristic sign of coli infection is a significant increase in body temperature.
Treatment involves prompt diagnosis and immediate antibiotic therapy. Furazolidone and ampicillin are used for this purpose.
Bird flu — a viral disease affecting the respiratory and digestive systems. It is transmitted by airborne droplets. The primary symptom is difficult to pinpoint. An infected hen becomes lethargic, loses appetite, and her wattles and comb turn blue. Difficulty breathing and significantly loose stools are also observed. There is no cure for this infection! Sick birds are culled.

Treatment involves the use of veterinary antiparasitic medications, including coccidotin, coccidiovit, and aveox. Adding fish oil to the food is recommended.
To prevent coccidiosis in the chicken coop, it is necessary to maintain sanitary and hygienic conditions and prevent dampness. Feed for the chickens must meet the required quality standards.
Helminthiasis
A group of diseases caused by helminths (worms). They are considered contagious.
Capillariasis — pathogens enter the bird's body through dirty water and feed of dubious quality. They parasitize the intestines, causing hens to lose their appetite and rapidly lose weight. In later stages, tail and wing spasms may be observed.
In the early stages, the disease responds well to treatment with phenothiazine. In advanced stages, treatment is pointless.

Cestodosia — a disease caused by tapeworm. Its symptoms include seizures and weight loss. Infection occurs through poor-quality food. Treatment is with the drug Filiksan.
Typhlogepatitis (histomoniasis) Histomoniasis is a parasitic infection that affects the liver and cecum. Symptoms are common to all helminthiasis: loss of appetite and weight, lethargy, and seizures. Affected chickens stop laying eggs. Histomoniasis is treated with furazolidone. Vitamins, especially vitamin A, are added to the birds' feed as a preventative measure.
Fungal diseases
These are contagious but pose less of a risk than infectious ones. Treatment almost always results in recovery, but if ignored, the affected animal may die. Infection occurs through contact between chickens and sick chickens.
Ringworm — affects the feathers and skin of birds. Pale yellow lesions appear on the comb and wattles. Later, feather loss and bowel problems occur, followed by rapid weight loss. Unfortunately, there is no treatment for this disease. Preventative measures include keeping the birdhouse clean.
Aspergillosis — a disease caused by mold fungi that affects the respiratory tract.
- Chickens cough and sneeze, and their breathing is noisy.
- Nasal discharge and bloody stools appear.
This pathology can be cured with copper sulfate, which must be added to the birds' water and food for several days.
Diseases caused by skin parasites

The easiest way to get rid of skin parasites is using stove ash. You can sprinkle it over the entire floor of the coop, or place a container filled with ash there. The chickens will roll in it, thus getting rid of the pests. There are also medicinal treatments using special products. Bars, Stomazon, and Frontline are available at veterinary pharmacies. However, when using them, it's important to strictly adhere to the dosage and frequency of application.
Effective and quite old is method of treating chickens' homes with dustBut this is a questionable method, since the dust can cause the death of animals due to its toxicity.
An important aspect of skin parasite control is treating all chicken coop inhabitants. To prevent skin parasites from bothering your birds, try to keep their housing clean. It's important to ensure that rodents, which are a reservoir for fleas, do not enter the coop. After purchasing your birds, it's recommended to inspect them, treat them with antiparasitic medications, and only then release them into the general coop.
You can get a more visual and complete understanding of chicken diseases, their prevention and treatment by watching this video.


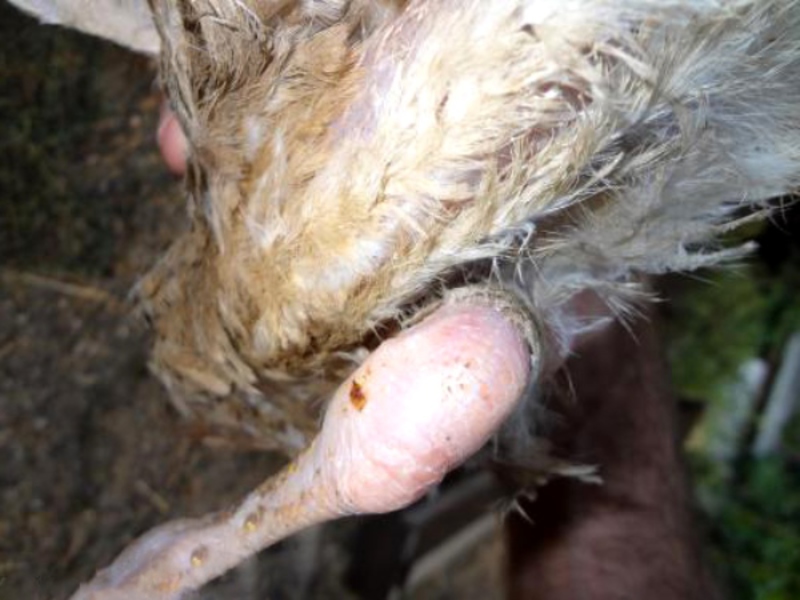


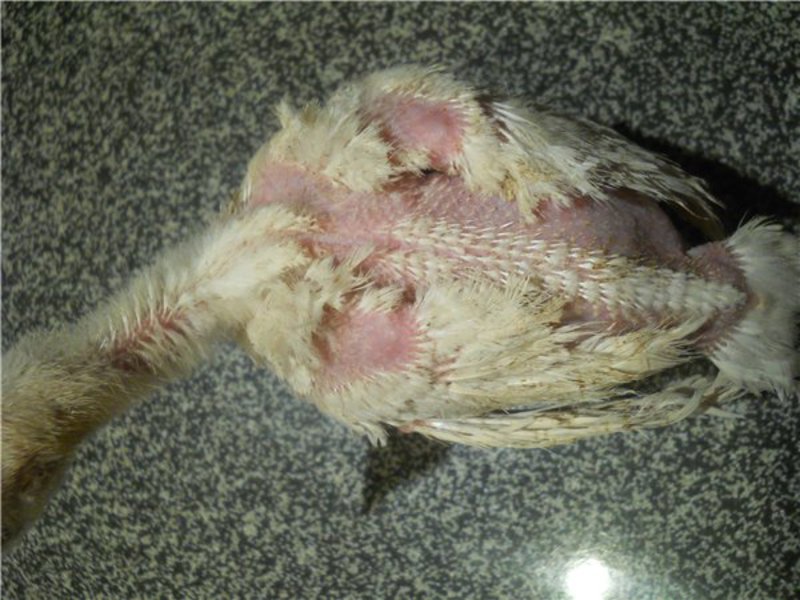



 feather cover (in healthy animals it is shiny and smooth)
feather cover (in healthy animals it is shiny and smooth)


1 comment