Oddly enough, sometimes the most harmful insects, which are also our immediate neighbors, can seem completely harmless. The carpet beetle is precisely such a type. Most of us don't even consider its existence, believing that this small black or brown bug causes no harm and is a temporary guest in our home. Unfortunately, only after realizing the damage caused by the carpet beetle do homeowners begin to consider getting rid of it.
Content
What are skin beetles: their types and developmental characteristics
Carpet beetles are one of the smallest pests living near us. Even an adult beetle doesn't exceed 9 millimeters in length, not to mention its microscopic larvae! The insect's body has a hard shell with three longitudinal stripes down the middle. Depending on the species, the beetle's color can range from black to light brown. The pest's body shape can be either round or oval.
The cycle of life
The reproductive capacity of these beetles is directly related to environmental conditions: the higher the temperature and the drier the air, the more vigorously they reproduce. A female can lay anywhere from several dozen to hundreds of eggs at a time, which hatch into larvae after about a month.
If environmental conditions worsen after hatching, insects at this stage of their life cycle are able to survive for 4–5 years without food, but the development of caterpillars simply does not occur.

The larvae of carpet beetles are practically omnivorous and do not sleep, so they are capable of ruining your things around the clock.
Within a year of birth, the caterpillar, if found in a suitable environment, transforms into an adult insect, undergoing approximately six molts. Under optimal conditions, the female lays eggs 5–6 times a year.
Video: The history of the distribution and development of the carpet beetle
Types of insects
There are approximately 600 species of carpet beetles. Of these, the most common in our country are:
- carpet beetles;
- fur beetles;
- Smirnov's skin-eaters;
- museum or house beetles;
- ham skinners;
- Frisch's kozhedy.
Carpet beetles
The carpet beetle family consists of three to four subspecies. These pests are small in size (2 to 9.5 mm) and have a brown body. Their primary food source is tiny organic particles:
- small crumbs left over from food;
- fragments of dog and cat hair;
- pieces of dead human epithelium (skin).
Interestingly, representatives of this species require food only during the larval stage, while grown carpet beetles use the nutrients and “fat” accumulated earlier to survive.
Fur beetles
Fur beetles are completely black, but have five white spots on their backs. They reach 4 to 6 mm in length. Despite their menacing name, this species feeds exclusively on food. Larvae can be found in forests, where they live in birds' nests and tree hollows, feeding on the corpses of various insects.
Smirnov's skin-eaters
Smirnov's carpet beetles typically reach no more than 3 millimeters in length. They are found primarily in window frames and on windowsills. Their larvae prefer to feed on dried fish, linen, wool, synthetics, and meat products.
House (museum) beetles
Museum (house) carpet beetles are most often found in stuffed animals and flowers, but are rarely seen in a house or apartment. Their body length ranges from 2.2 to 3.5 mm. These insects received their name because they have destroyed a record number of exhibition exhibits since Carl Linnaeus discovered them in a Swedish museum.
Frisch's skin beetles
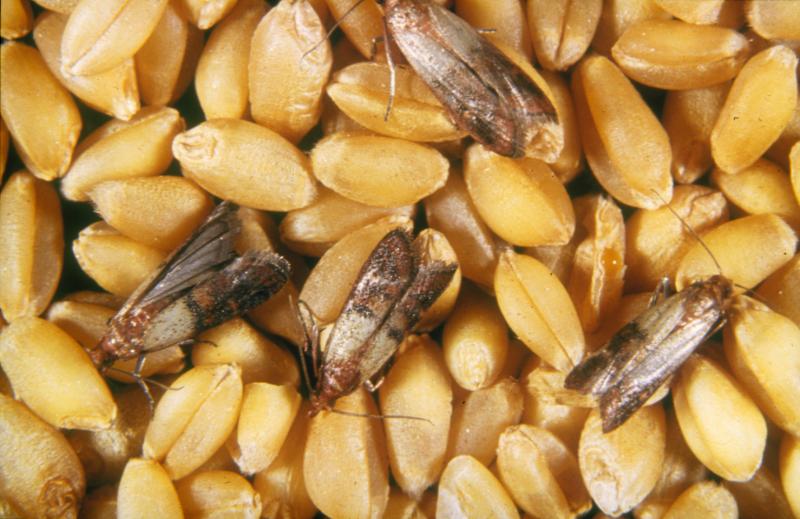
Members of this species reach 6 to 9 mm in length. Their bodies are matte black and oval. The larvae are blackish-brown and densely covered with hairs. Both early-stage and adult larvae cause harm to humans. They feed on leather goods, grain, flour products, and cocoa beans, and will also consume animal feed and meat and bone meal.
Photo gallery: Types of carpet beetles
- Carpet beetle larvae can crawl right under your feet, devouring your carpeting.
- Smirnov's skin beetles can eat your clothes, whether made from natural or synthetic fabrics.
- Museum skin-eaters love to eat stuffed animals and botanical collections.
- Frisch's leather beetle larvae will happily feast on your leather boots, as well as anything they find in your kitchen cabinets.
- The fur beetle is one of the most harmless species, most often found in forests.
How insects get into your home and what damage they cause
Like many other insect pests, carpet beetles have their own, and quite a few, ways to enter our homes. For example, they can enter from an infested room along with household items and belongings, in a potted plant, and so on.
The bugs can also simply fly in through an open window or door during the warmer months. There are various reasons why carpet beetles appear in your home, but they are most often attracted by a dry indoor climate and the availability of food.
Damage from carpet beetles
The greatest damage to our household items is caused by the larvae of the carpet beetle, although in some subspecies, adult beetles are no less destructive. The following are most often affected:
- leather book covers and other leather goods;
- carpets and rugs, especially made of wool;
- fur coats made of natural fur;
- food products;
- botanical collections, stuffed animals and other exhibits.
It's worth noting that carpet beetle larvae have absolutely no need for sleep, and their gluttony is simply phenomenal, so they spend 24/7 gnawing on everything they can find.
However, these beetles are dangerous not only for your household items. Insects can also harm you personally. Carpet beetles and their larvae can bite humans, which can lead to helminth infestation and various infections. A bite appears as a small red spot anywhere on the body, although those prone to allergic reactions can have a significant size. If you find something similar on your body, treat the affected area as soon as possible with a disinfectant (alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, etc.).
How to tell if you have carpet beetles in your home: the main signs
To effectively combat carpet beetles, you need to be sure they're the real deal. You can recognize their presence in your home by certain signs:
- After the pests molt, chitinous shells remain;
- holes appear on things and household items made from organic and natural materials;
- in secluded places of the home, granules of larval feces are found;
- On a fur product or carpet you saw a brownish or black beetle, or a brownish-colored individual in the first stage of development, covered with tufts of bristles.
Larvae, like young beetles, don't tolerate light well, so they're most often found in shaded or dark corners of the home. They often nest in places like:
- kitchen cabinets containing cereals and flour;
- carpeting;
- upholstered furniture;
- things made of fur and wool.
Colonies of carpet beetles can be found behind baseboards, wallpaper that has come loose from the walls, in ventilation systems, in the attic, etc.
How to get rid of pests
Once you've determined that carpet beetles are the ones damaging your belongings, it's time to think about how to get rid of these tiny pests. If you prefer speed and guaranteed effectiveness, you can opt for chemical treatments. However, if safety is your top priority, try using natural remedies. But first, try physical methods to eliminate the insects.
Physical methods of elimination
For physical removal of carpet beetles, a steam cleaner is best. Use it on carpets and rugs, upholstered furniture, curtains, and any other items that won't be damaged by water or hot steam. If you don't have one, vacuum all soft surfaces thoroughly.
Wash floors and baseboards as often as possible, preferably once or twice during the entire period of pest control. Items and food that have been severely damaged by carpet beetles should be burned or simply thrown away. It's best to wash upholstered furniture covers and bed linens in very hot water.
Chemicals for combating carpet beetles
The most effective active ingredients in the fight against carpet beetles are allethrin, chlorpyrifos and bendiocarb. However, when using drugs, never forget about their toxicity to pets and people. They should be used in strict accordance with the instructions and in protective equipment (gloves, respirator, closed clothing).
During treatment, pay attention not only to damaged items and carpeting, but also to hidden spots such as under the bed and behind the closet, various cracks and crevices, and baseboards. This will help disinfect all potential pest breeding areas.
If you are using a solution, you can add an insect growth regulator to it for greater effectiveness, which limits the ability of carpet beetles to reproduce.
Chemicals can be produced in various forms:
- powder preparations;
- sprays;
- pills;
- liquid emulsions.
Powder
The powdered product is sprinkled into areas where carpet beetles may live: cracks, spaces behind and inside cabinets, baseboards, etc. The easiest way to do this is with a broom.
Spray
Aerosols (Karbofos, Raid, Chisty Dom, Raptor, etc.) kill beetles and larvae but do not harm the eggs, so they should be used at least twice, 2-3 weeks apart. They are sprayed over all surfaces in the room and the results should be visible in about a month. The active ingredient in the product, when it comes into contact with the insect's shell, causes paralysis and death. Naturally, larvae, lacking a chitinous shell, die faster.

Raptor aerosol is a reliable and effective remedy for fighting crawling insects, including carpet beetles.
Liquid emulsion
Liquid concentrates (Tetrix, Palach) are best used in homes heavily infested with pests. This is because these products are highly toxic, killing both adult pests and eggs and larvae. They should only be used while wearing protective equipment.
Apply the product to all surfaces and objects and leave it on for at least 2 hours, then rinse. If the room is unoccupied, the product can be left on for up to a month. Pests disappear within 1–3 weeks, and the residual effect lasts up to 1 month.
If you are concerned about the product leaving marks on an expensive item, place it in a plastic bag and carefully place the opened bottle of the product in there for 2 hours.
Poisonous pills
Methods using tablets (such as Antimol) are effective against larvae but will not affect adult pests, as they may not consume solid food at all. This method can be used as a supplementary measure. The obvious downside is that the tablets' effects will only become apparent after a long period of time, and the pungent odor will be absorbed into all surrounding household items.
Folk remedies
Home remedies for insect control aren't always easy to use, but if you don't want to use chemicals, you have no choice.
Freezing
Carpet beetles love comfortable living conditions, so temperatures below -10 OIt's fatal to them. To get rid of this pest, you can open all windows and doors wide during cold weather and ventilate the room for 3-4 hours. Repeat this procedure several times, alternating it with wet cleaning. Beforehand, wrap all pipes in the home with foam sheets or rags to prevent them from bursting. If you plan to freeze a specific item, wrap it in a plastic bag and place it in the freezer for 2 hours.
Steam treatment
All surfaces, clothing, and upholstered furniture can be treated with a steam generator to kill adult flies and their larvae. This procedure is usually repeated after 2-3 weeks to completely eliminate the problem.
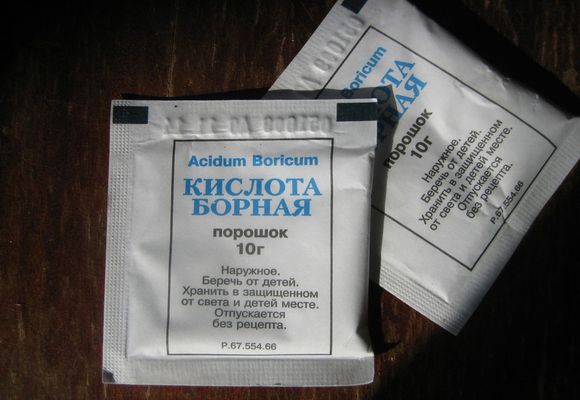
Boric acid
A virtually universal pest control agent, boric acid, is sprinkled on a sheet of paper and placed under cabinets, beds, and sofas, and then left to take effect.
Strong aromas
Cotton swabs soaked in tansy, lavender, and lemon balm essential oils, which repel skin beetles, can be placed on cabinet shelves.
Vinegar
The smell of vinegar is highly repulsive to insects and repels them, so use a solution of this solution (one tablespoon of vinegar per liter of hot water). Use a spray bottle to spray all cabinets, windowsills, frames, shelves, and baseboards.
Video: How to get rid of carpet beetle larvae
Prevention of the appearance of skin beetles
Once you've gotten rid of these pests, you should take all possible measures to prevent them from returning. Therefore, follow these steps:
- During the off-season, it is advisable to store leather and fur clothing in vacuum bags or with moth tablets or naphthalene; cedar shavings also repel skin beetles well;
- All cracks in window sills and frames should be sealed, mosquito nets should be attached to the windows, and fine mesh should be installed on the ventilation openings;
- Carpets and rugs should be cleaned regularly to minimize the possibility of carpet beetles appearing there;
- It is advisable to check cereals, crackers and flour purchased in bulk for the presence of bugs and larvae, and store uninfected products in tightly sealed containers;
- It is worth performing wet cleaning more often; the best option for preventing the appearance of skin beetles is to clean all surfaces with a steam generator;
- dried lavender or wormwood flowers should be placed in bedside tables and cabinets;
- It is advisable to get rid of things that no one uses as often as possible.
Although carpet beetle larvae can cause serious damage to property, if you detect these "neighbors" early, you have a good chance of getting rid of them. However, it's still better to avoid their presence altogether through preventative measures.