Scabies is considered one of the oldest contagious skin diseases. It was described in ancient times, approximately 2,000 years ago. Everyone is susceptible to this disease, regardless of age, gender, origin, or race. Medieval scientists assumed the disease was parasitic in origin, but with the advent of the first microscope, luminaries of medicine demonstrated the involvement of the scabies mite. Infection occurs through close contact with an infected person, as well as through sexual contact, handshaking, and sharing personal items. The mite adapts to various conditions, be it heat or cold, and can survive in humid environments for up to 5 days.
Content
What is scabies?
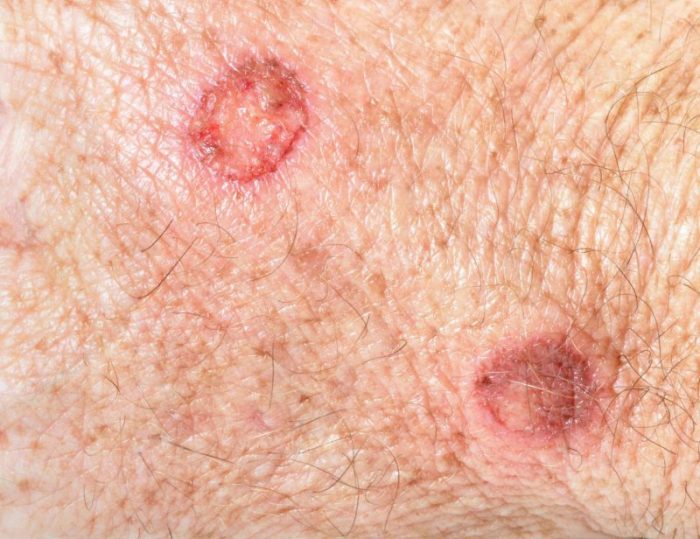
Scabies is a serious skin disease caused by the itch mite (Sarcoptes scabiei), also known as the itch mite. The condition is characterized by persistent, intense itching, especially at night and after bathing, due to increased mite activity, as well as a rash (which, in advanced cases, can develop into pustules). This rash indicates an infection acquired through scratching.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Since scabies is a dermatological condition, the first thing a person should do is be wary of itching and consult a dermatologist, as these symptoms can easily be mistaken for an allergic reaction. When itching occurs, people often self-diagnose and self-medicate without seeking medical help.
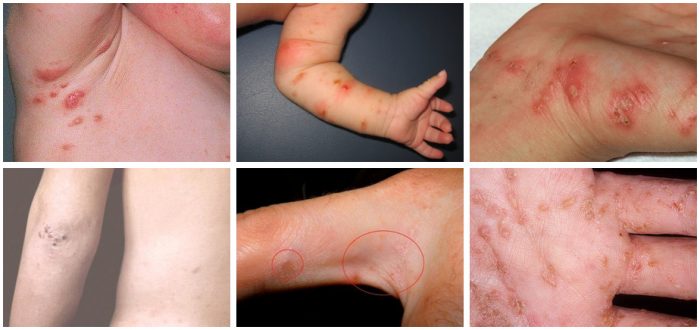
First of all, you should be wary if a rash appears in the form of pimples, blisters, pustules, as well as paired, zigzag passages and scratches characteristic of the scabies mite.
Where can the rashes appear?
Symptoms of the disease can appear on any area of the skin in both children and adults. However, the tick prefers warmer areas, such as under watches and tight-fitting clothing. The parasite's favorite places to nest are skin folds, the spaces between the toes and fingers, the lower abdomen, and the folds of the knees and elbows.
Signs of scabies rashes can be noticed:
- in the groin area;
- lower abdomen;
- under the arms;
- in the folds of the arms and legs;
- on the bends of the knees;
- on the shoulder blades;
- around the nipples.
Causes of the disease and its pathogen
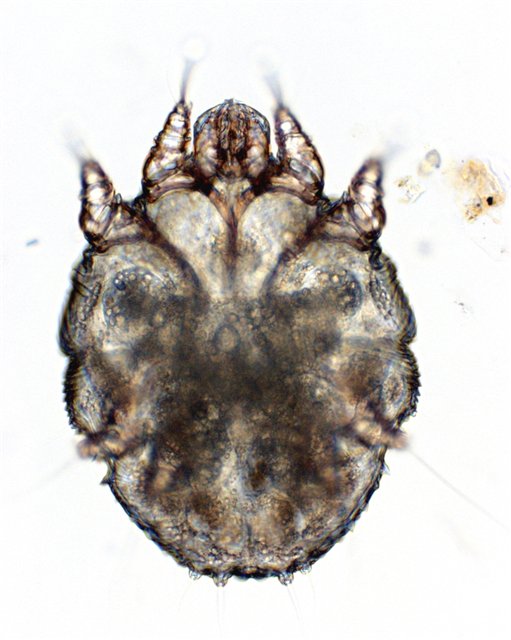
The causative agent of scabies is the female mite. It measures 0.3–0.4 mm. It has an elongated, oval body, resembling a bean. Its back is lined with numerous spines on either side of a transverse slit, and its hind legs have flagellum-like setae. The female lays eggs through a slit located on its abdomen. The male is slightly smaller than the female and has scales and setae on its back. Its front legs have suckers that help it move forward. It has two hind legs and two front legs, a proboscis with suckers, and multiple joints. The mouth is located in the middle, between the legs.
The tick digs tunnels using three claws located at the tip of its proboscis.
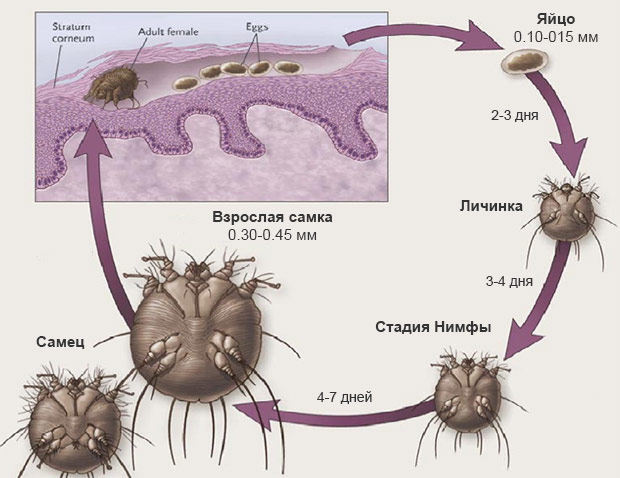
The female digs tunnels on the skin's surface beneath the epidermis, laying 2-3 eggs daily. After a couple of days, the larvae hatch, becoming nymphs after 3-4 days. The nymphs mature into sexually mature adults within 2 weeks. The lifespan of an adult female is 1 month.
Scabies can easily be confused with dermatological diseases such as lichen, allergies, rubella, and dermatitis, since they are similar in appearance. However, when examined under a microscope, subcutaneous passages are observed, which are the main difference between scabies and other skin diseases.
What harm can scabies mites cause?
Ticks can carry various dangerous diseases that cause significant harm to humans and animals.
Types of scabies mites:
- Demodex brevix and Demodex folliculorum cause demodicosis in humans;
- Demodex canis is the causative agent of demodicosis in dogs;
- Sarcoptes scabiei is an itch mite that infects dogs, humans, and sometimes cats;
- Sarcoptes canis - causes sarcoptes in dogs;
- Otodectes cynotis is the causative agent of ear mites, or otodectosis. It lives only in the ear and dies upon contact with the skin.
- Notoedres cati causes notoedrosis. It hides under the skin of rabbits, cats, and dogs. It is transmitted to humans.
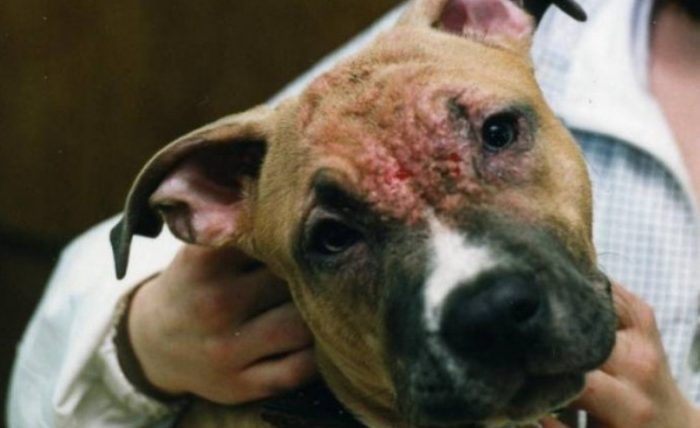
Pets are at risk of contracting scabies, which is transmitted from an infected animal to a healthy animal through direct contact. It's painful to watch your pet, tormented by constant itching, scratching at the bites and licking the affected areas. This behavior is caused by the mite, which causes scabies.
Different types of scabies in animals
Sarcoptic mange is caused by the mite Sarcoptes canis. It spreads to pets through contact with an infected animal. The disease is not very dangerous, and if promptly treated by a veterinarian, it is easily treated. In advanced stages, sarcoptic mange can lead to adverse effects, including death.
Symptoms of a Sarcoptes canis tick bite:
- the pet is constantly scratching itself, fidgeting, and won’t sit still;
- wounds on the body, scratches with bruises, crusts, ulcers;
- there is dandruff in the bite area;
- hair loss, rough skin of red or gray color;
- twitching of the hind legs when the owner wants to touch the ear;
- loss of appetite, worsening sleep.
Scabies mites feed and live only on animals. If they come into contact with a human body, they die of starvation because they are unable to burrow beneath the skin.
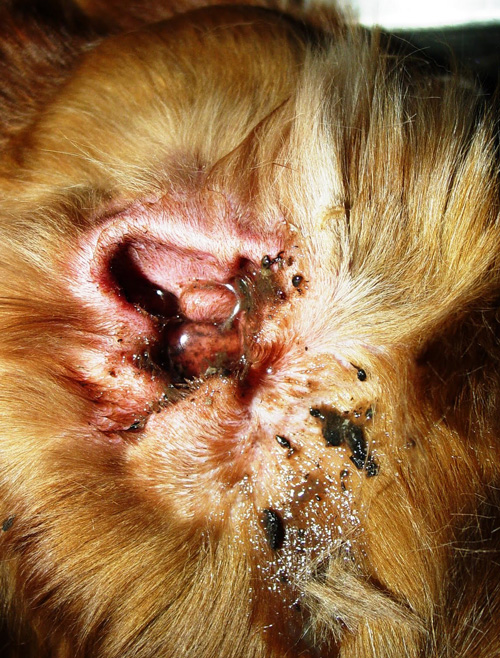
Another dangerous parasite is the ear mite, which is rarely found in humans. Their favorite habitat is the ears of dogs and cats. An animal can bring the parasite home from the street or become infected through contact with an infected pet. Ear mites are not harmful to humans, as they die upon contact with the body. The mite feeds on earwax and sebum, causing itching when moving around in the ear, causing discomfort to the dog. The mite's lifespan is no more than two months.
Signs of ear mites:
- the animal, trying to get rid of a foreign body in the ear, shakes its head;
- bleeding wounds that fester over time are caused by constant scratching;
- the dog tilts its head towards the sore ear;
- A dark sticky mass resembling pieces of earth with an unpleasant odor is visible in the ear.
Notoedric mange is a disease caused by parasitic mites. It is characterized by profuse hair loss and the appearance of rough growths on the skin. The mites infest the head and then migrate to the neck and ears. At the first sign of symptoms, consult a doctor, as notoedric mange is a dangerous disease that can be transmitted to humans.
Symptoms of notoedrosis:
- the appearance of blisters and ulcers;
- folds form on the skin;
- severe itching;
- hair loss;
- grey-yellow wrinkled skin.
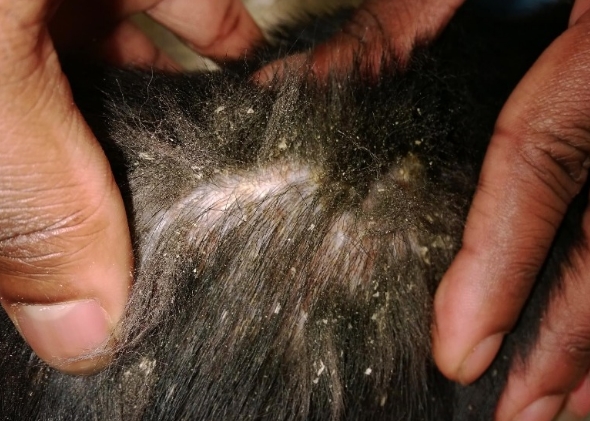
Demodicosis is a disease caused by the mite Demodex canis. It occurs in dogs with weakened immune systems.
This disease is not transmitted to humans from animals.
Demodicosis is divided into a localized form (mainly in puppies) and generalized (in adult dogs with multiple skin lesions).
Symptoms of demodicosis:
- itching is strong or weak, depending on the form of the lesion;
- dandruff;
- the skin is inflamed, red;
- ulcers, crusts at the affected areas;
- partial baldness.
How to treat scabies in animals
Before treating scabies at home, the affected animal should be isolated from other pets and family members. With prompt action and early treatment, scabies is relatively easy to cure.
Treatment regimens for pets
Remember that only a veterinarian should diagnose and prescribe treatment. The main medications that help combat the disease are:
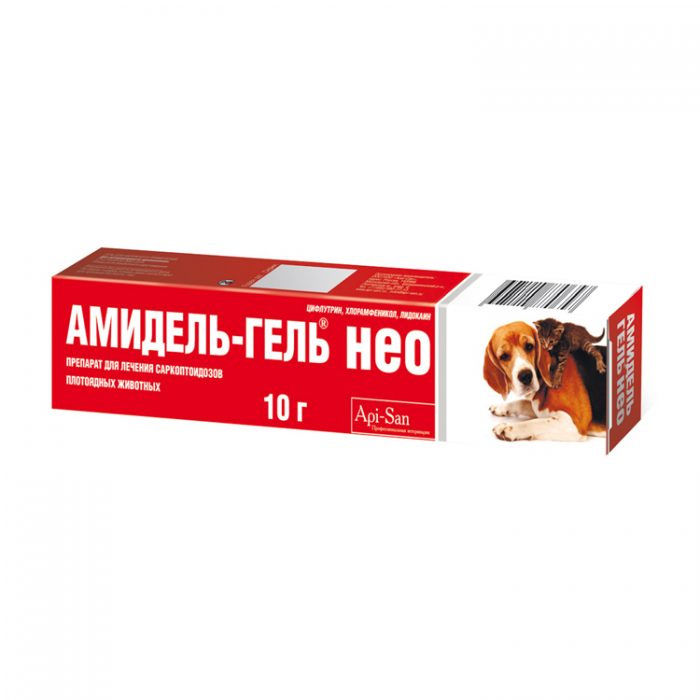
- Amidel Neo gel is used in the early stages of the disease. This is the simplest way to treat scabies. In advanced cases, Amidel is used with Ivermectin injections. The gel is safe for dogs. It helps relieve pain, reduce itching, and reduce inflammation. It contains chloramphenicol, an antibacterial agent that does not cause dysbiosis in animals. Amidel gel is applied to the affected areas 2 to 5 times at 7-day intervals. If there are rough crusts on the animal's skin, they are removed. To allow access to the inflamed areas, the fur is shaved or clipped. Painkillers such as lidocaine and novocaine are used for pain relief. Antiparasitic agents are also used: Advantage, Stronghold based on selemactin.
- Additionally, you can lubricate the affected areas with 60% sodium thiosulfate. Before the procedure, put a collar on the dog to prevent it from licking the ointment.
- If the drugs described above are not available, Ivomec can be administered subcutaneously.
Before buying a dog scabies medication yourself, it's best to consult a veterinarian, as severe itching may be caused by a food allergy rather than a mite. To confirm the diagnosis, a scraping from the affected area is necessary. The test may not immediately confirm the diagnosis if the parasite has penetrated deeply under the skin or if the scraping was taken from the wrong location.
To avoid complications, the doctor prescribes vaccines against fungi, antibiotics, and vitamins to support immunity and improve hair growth.
Folk remedies (iodine, apple cider vinegar, alcohol) are of little use and often worsen the dog's condition. Sulfur ointment is used as an exception. It should be applied frequently. To prevent the dog from licking the ointment, a muzzle or collar should be placed on the dog. Garlic infusion is not recommended, as it is toxic in large doses.
The only folk remedy that is used in parallel with the main treatment of demodicosis is lavender oil.
Video: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Demodicosis in Dogs
Preventive measures
To ensure a quick recovery of your pet, it is very important to follow basic hygiene rules:
- wash the floors daily, ventilate the sick animal’s room;
- change and wash the bedding frequently in bleach, iron and dry outside;
- treat your pet's dishes;
- limit contact between children and other four-legged friends with the injured friend;
- examine your skin regularly;
- bathe your pet in a timely manner and maintain hygiene;
- avoid contact with stray dogs;
- follow the principles of proper nutrition.
With proper preventative measures and veterinarian recommendations, scabies can be cured fairly quickly. After recovery, your pet should boost their immune system with multivitamins and a balanced diet, constantly monitor their skin, and, if necessary, consult a specialist.