Anyone who decides to breed rabbits inevitably faces the question of how to build a comfortable cage for their rodents. Housing for these long-eared creatures can be designed in a variety of ways, and can be either factory-made or homemade. We'll focus on the latter option.
Content
What materials can it be made from?
When planning the construction of rabbit hutches, the first thing to consider is the selection of suitable building materials. In principle, any readily available materials will suffice for constructing a simple structure that will protect the animals from adverse environmental factors.
Wood and metal, galvanized steel, plastic elements, bricks, clay, and even industrial pallets are used in the construction of rabbit farms. Although virtually any material is suitable, their selection should be approached with the utmost care.
Wood
Wood is widely used in rabbit hutch construction. It can be used to create any structural element. The frame of the hutch is typically made from lumber. Wooden plank floors are also popular among rabbit breeders.
The main advantages of the material are its environmental friendliness and ease of processing.Wooden elements can be easily molded into virtually any shape. Wood's excellent thermal insulation properties are also worth considering: a wooden rabbit hutch will be warm in winter and not too hot in summer.
One drawback worth mentioning is their rapid deterioration. Rabbits love to chew everything, so wooden elements of the cage's interior are quickly destroyed by rodents. Furthermore, wood, due to its porous structure, absorbs all odors and liquids, so a solid wooden floor is not recommended for the cage.
Important! Insects and moisture also contribute to rapid wood deterioration, so all wooden structural elements must be treated with protective compounds. When choosing a compound, ensure it is safe for animals.
Metal
Metal is a more durable construction material than wood.Rabbits can't chew through metal parts, they're easy to clean, and they're not afraid of insects. However, working with metal requires special skills and the ability to handle specialized tools.
The frame of the future cage is made of metal pipes. Metal is also used for the interior trim of wooden cages to prevent chewing through the natural material. However, it is not recommended to make the roof and outer walls of the cage out of metal, as they can become very hot in the sun and freeze in the cold, posing a health risk to the eared inhabitants.
Galvanized profile
Galvanized profiles are used in combination with other materials. Unlike solid metal elements, reinforcing or finishing the cage with profiles does not add weight to the structure, which is especially important for portable, mobile rabbit hutches.
Plastic elements
Plastic pipes can be an alternative to wooden beams and metal pipes. This durable and lightweight material allows for the creation of versatile cages suitable for use in any environment.
When working with plastic, it's important to keep animal safety in mind. Internal components that rabbits might chew should not be made of plastic. The animal could injure its mouth or esophagus with splinters, or be poisoned by the synthetic substances contained in the material.
Important! When exposed to strong heat (for example, in hot weather), some types of plastic release toxic substances.
Bricks and clay
Bricks and clay are used to build rabbit hutches, mainly in hot regions.The foundations of the houses are laid with bricks, and the joints are sealed with clay. This type of cage protects the animals well from overheating, as brick has excellent thermal insulation properties.
Net
Rabbit cage walls can be solid, made of slatted bars, or wire mesh. Wire mesh is considered the most convenient option, and should have medium or small mesh openings and be sufficiently strong.
Slate
The most practical material for a rabbit hutch roof is slate. It provides excellent protection without overheating in the sun or being moisture-resistant.
Materials at hand
Rabbits aren't the most fussy animals to care for. Houses made from scrap materials are ideal for temporary housing or when budgets are tight. Inventive rabbit breeders repurpose old barrels and containers for rodent housing, or construct multi-story structures from industrial pallets.
Each material has unique properties that can be both an advantage and a disadvantage. When choosing, consider the advice of experienced rabbit breeders, individual conditions (climate, breed, etc.), and the instructions for popular designs, if you plan to use them.
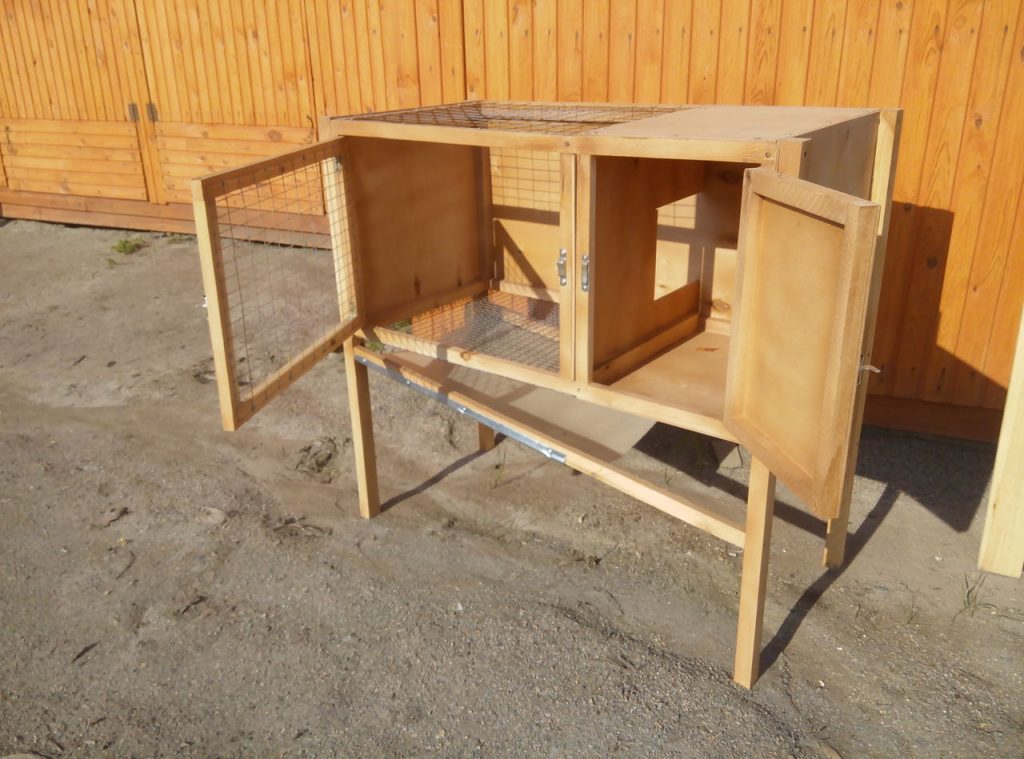
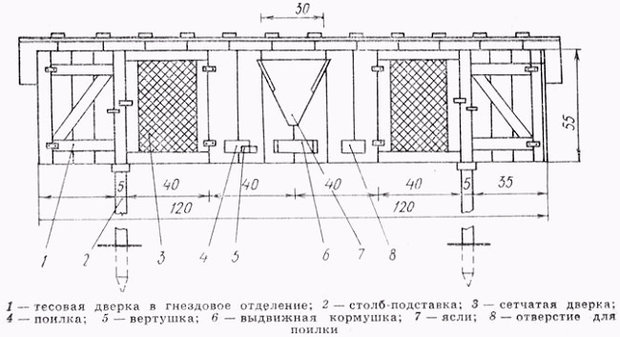
A typical rabbit cage made by hand
There are many different types of rabbit cages, varying in the number of tiers and sections, sizes, and the presence of amenities such as feeders and waterers. Designs like those by Zolotukhin or Mikhailov are easy to find online.
If we talk about a typical cage for adult rabbits, the optimal parameters would be the following dimensions:
- Length - 120-150 cm;
- Width - 60–80 cm;
- Height - 60 cm.
To conserve material and improve maintenance, it's recommended to build paired cages. This will increase the length to 3 meters.
Don't skimp on space by making cages smaller. Animals need enough space, otherwise they become sedentary, become ill, and stop producing offspring.
In appearance, a typical cage resembles a block consisting of two sections, each of which can contain one adult individual.The most commonly used materials in construction are wood and plywood for the frame and interior finishes, fine-mesh metal mesh for walls and partitions, and slate for roofing.
Cage floors are rarely solid. They're typically constructed from narrow slats or mesh, as this simplifies rodent maintenance. Rabbits produce a lot of waste, which ends up in a specially installed tray through a mesh or slatted floor. Solid flooring requires frequent cleaning.
Necessary tools and materials
To make a typical cage you will need the following materials:
- Wooden beams - 10 pieces, size 300x3x5 cm;
- Plywood sheets - 2 pieces, size 150x150x0.1 cm;
- Metal mesh - 3 m with a cell size no larger than 15 mm;
- Self-tapping screws - approximately 2 kg. You will need sizes 3 and 7 cm;
- Fittings - door hinges and latches;
- Perhaps wooden floor slats as an alternative to metal mesh.
Tools for work:
- Hand saw or grinder;
- Metal scissors or nippers;
- A screwdriver or hammer with nails (instead of screws);
- Tape measure, pencil, level.
Drawing
The drawing shows all the main elements of the structure and indicates the dimensions in cm.
Manufacturing instructions
- Construction should begin with constructing the frame. It is assembled from timber, cut to size and fastened with screws or nails. If possible, it is recommended to recess the frame's legs into the ground for greater stability.
- The floor of the future cage is constructed from slats, leaving 0.5–1 cm gaps between them, or using wire mesh. The closed nesting compartments on the sides of the cage can be made solid using plywood.
- The back and side walls of the cage and the feeder are also made from plywood.
- After making the doors using metal mesh and wood scraps, they should be secured with hardware.
- Finally, the cage is covered with a roof. Depending on the external conditions, a double roof (plywood and slate on top) is installed or simply covered with slate.
Video: DIY Standard Rabbit Cage
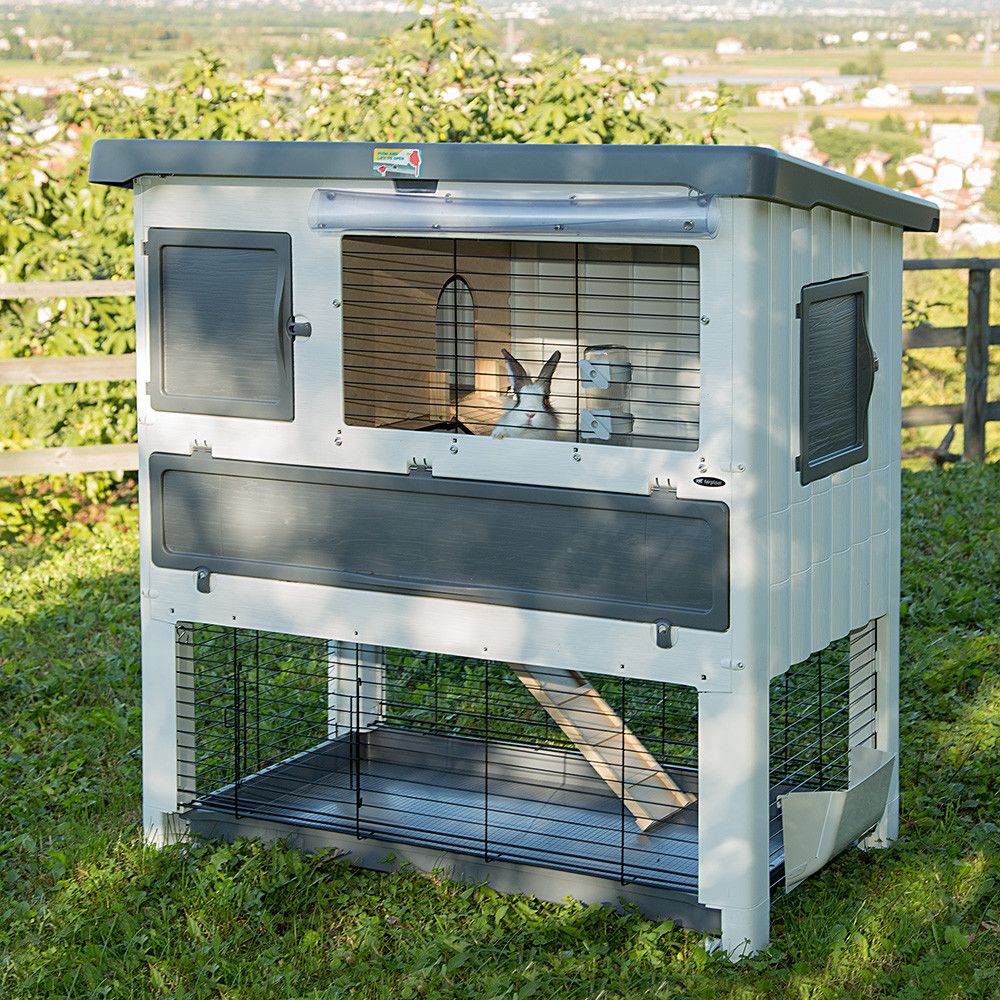
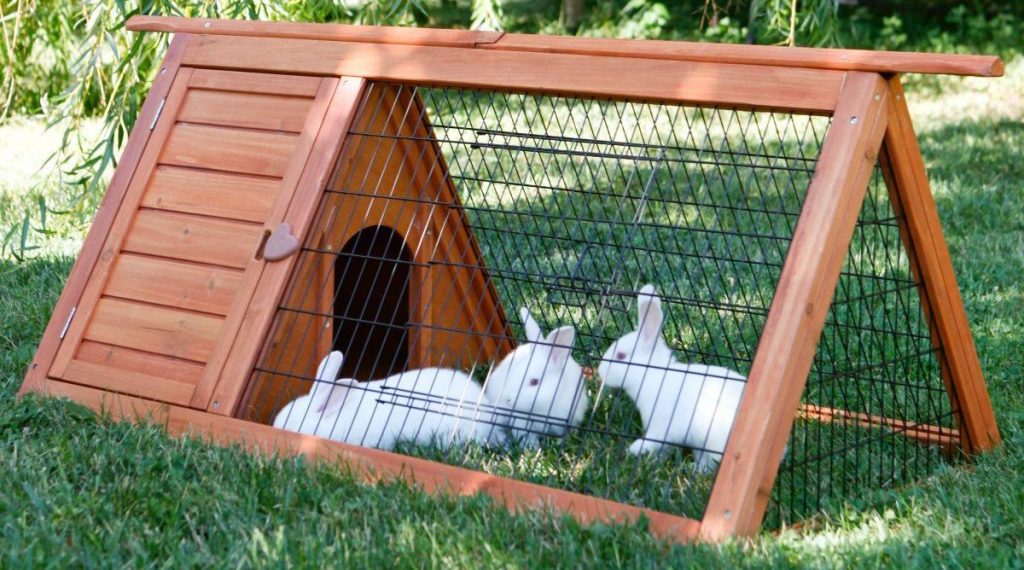
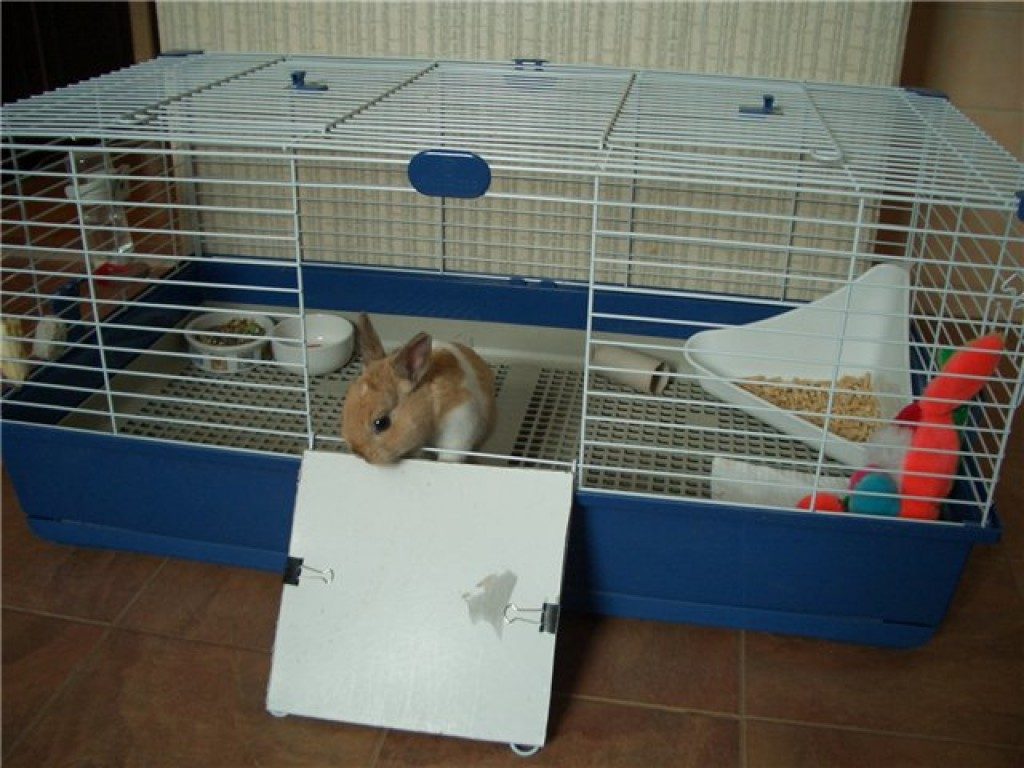
Cage for decorative rabbits
The more spacious the home for a pet rabbit, the better. Two-story structures or run-in areas can also provide comfort. Decorative rabbits are usually kept indoors, so the requirements for thermal insulation and protection from external factors for the housing structure are much lower..
The flooring in a cage for decorative rabbit breeds should be solid and soft. The paw surfaces of decorative rodents are prone to inflammation and deformation because they lack soft pads. A wooden floor lined with a soft, absorbent material (sawdust, special wood filler, soft straw, absorbent pads, etc.) is ideal.
Necessary tools and materials
The manufacture of a cage for keeping decorative rabbits involves the use of the following materials:
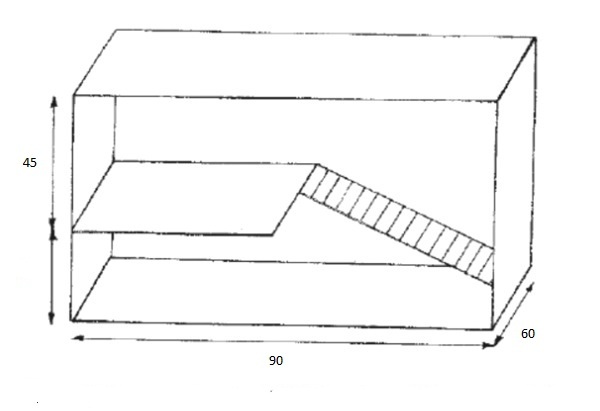
- Sheets of plywood, chipboard or wooden panels: it is better to take some in reserve, focusing on the dimensions of the cage (90x60x45 cm);
- Metal sheet (you can use tin): 90x60 cm;
- Wooden slats;
- Metal mesh: 60x45 cm minimum;
- Self-tapping screws or nails;
- Door fittings.
Tools for work:
- Saw, hacksaw or jigsaw;
- Screwdriver or hammer;
- Nippers or metal scissors;
Drawing
Dimensions in the drawing are given in centimeters. The cage size and design are optimal for housing one adult individual in a heated room.
Manufacturing instructions
- Construction of a rabbit hutch begins with the floor. A 90x60 cm base is cut from chipboard or a wooden board.
- A metal shield of similar dimensions is placed on a wooden base.
- Then, from wood or chipboard, wall panels are prepared with dimensions of 45x60 cm.
- The frame is assembled using nails or screws.
- The door is made of wooden slats and metal mesh. The optimal size for the door is 30x30 cm.
- The second tier is made of the same material as the walls and is installed inside the cage.
- The staircase is made from slats, keeping the width at least 15 cm, and is installed close to the second tier, carefully securing it.
A cage for keeping decorative rabbits is fairly easy to build. Even novice rabbit breeders with no experience in construction or design can handle the task. Painting the cage's surfaces with paint or varnish is not recommended, as rodents can be poisoned by toxic substances when chewing through the structure.
Video: DIY Two-Story Rabbit Cage
Design features
All rabbit hutches are designed according to general principles, but different types of shelters have their own unique characteristics. Design nuances depend primarily on the breeds and individuals the breeder plans to keep. Any production farm houses several groups of rabbits of different ages and even breeds.
Depending on whether the rabbit hutch will be located outdoors or indoors, you should select suitable construction materials and plan the structure's dimensions. Hutches can have from one to three tiers and an unlimited number of sections in length.
Rabbits of different ages (newborns, young rabbits, and adults) require special housing conditions, and their cages will therefore differ. For example, pregnant females with newborn kits are kept in special mother cages with nests.
Cages should be sized to provide the animals with sufficient space and room to move around. Obviously, cages for giant and dwarf rabbits will differ greatly.
Depending on the size of the rabbits
The optimal dimensions for a spacious cage that houses a pair of adult rabbits of standard size are:
- Length: 120–170 cm;
- Width - 60–80 cm;
- Height: 50–60 cm.
Dwarf and decorative (up to 4–5 kg) rabbits will benefit from more modest conditions:
- Length - 70-90 cm;
- Width - 35–55 cm;
- Height: 30–50 cm.
Giant rabbits will require much more space:
- Length: 85–100 cm;
- Width - 70–80 cm;
- Height: 60–80 cm.
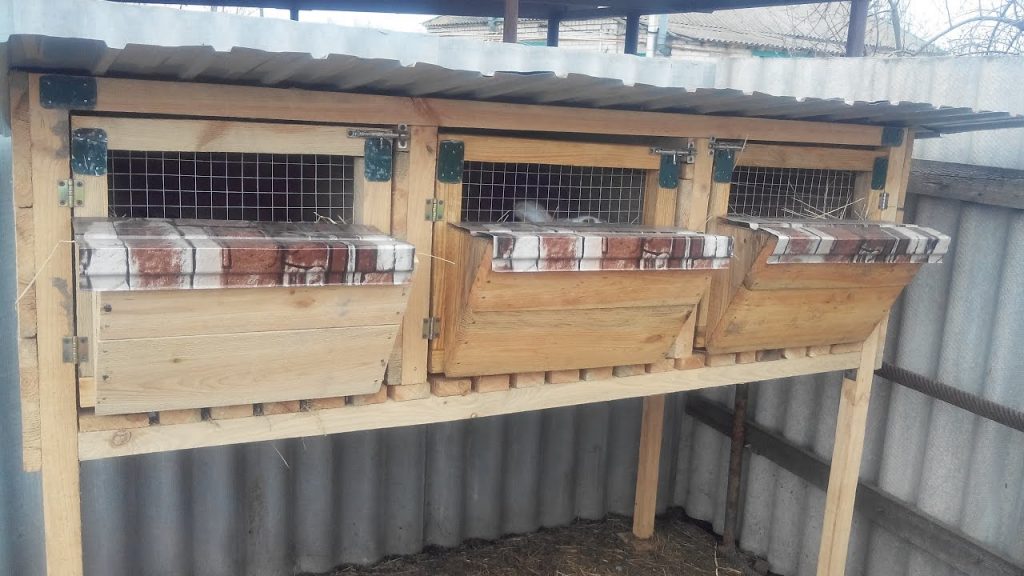
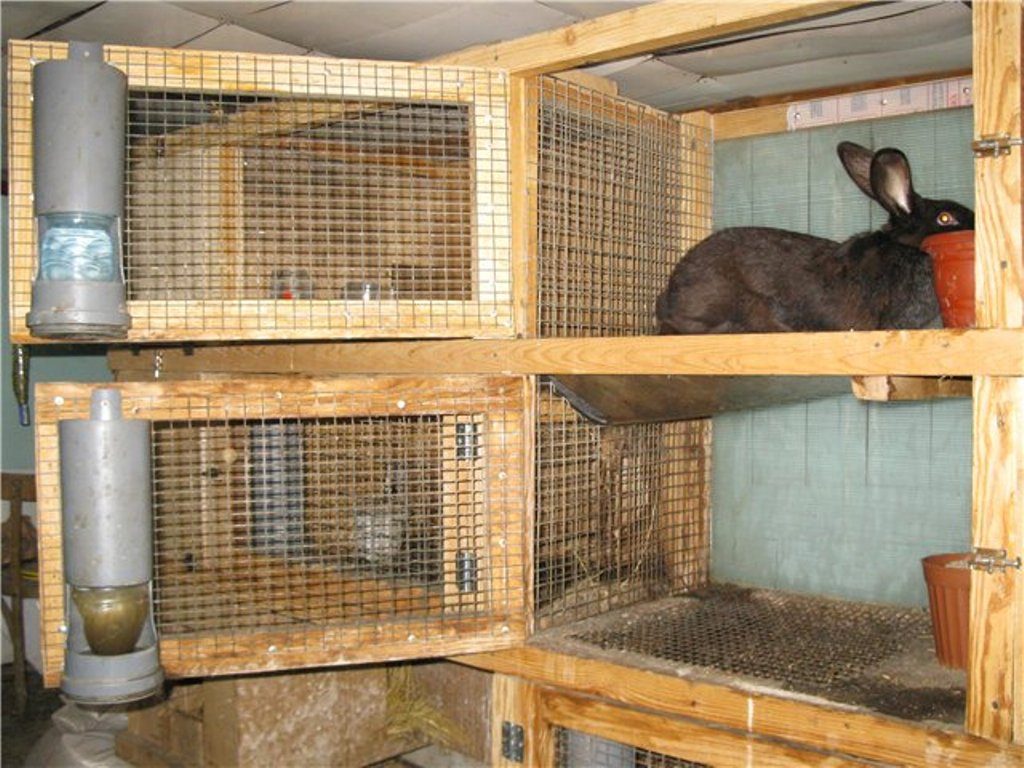
Multi-tiered cells
Productive rabbit farming involves keeping a large number of rodents of different sexes and ages at the same time. Multi-tiered housing structures come to the rescue of rabbit breeders. Cages are installed in both two and three tiers. Multi-tiered rabbit cages are permanent structures, yet relatively easy to build yourself.
Multi-tiered cages designed by Zolotukhin are popular among rabbit farm owners. They offer several advantages:
- Capacity;
- The ability to keep all representatives of rabbit families (females, young animals and males) in one place;
- The animals are easy to care for;
- Zolotukhin's cells are quite mobile - they can be moved from place to place.
Depending on the purpose
Depending on their purpose, rabbit cages are divided into several types, each of which has its own design features:
- A standard cage for permanent housing. You can easily find a drawing of such a cage online, making it easy to build your rodent home yourself. Pay attention to the cage's dimensions, which shouldn't be too small, and the safety of the materials;
- The breeding cage should be much more spacious, since several individuals will be in it at the same time;
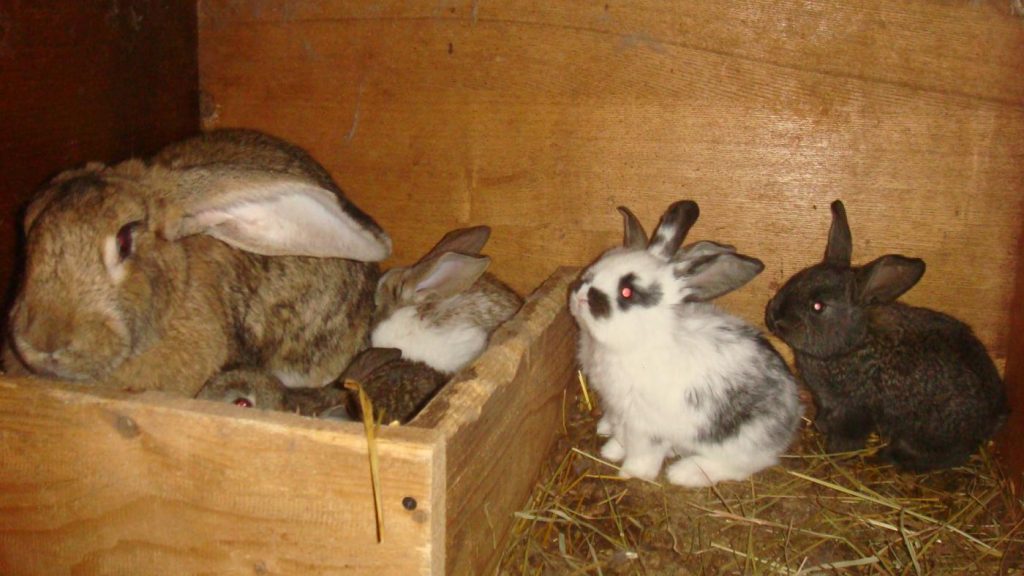
- A special type of home for a doe with her kits or a pregnant female rabbit is called a nest box. A secluded area and warmth are the two main components of comfort for a pregnant doe and her newborn kits. A nest box typically has solid walls, a unique nest box that mimics a cramped burrow, and facilities for nursing the mother.
- A juvenile cage meets standard requirements, but is often equipped with an additional run for exercise. This opportunity to stretch a little is beneficial for the growth and development of the young animals. The run is made of wire mesh and often provides the animals with access to fresh grass.
Depending on the climate and time of year
The optimal ambient temperature for rabbits to feel well is 14–16 degrees. Maintaining a normal climate in the houses and protecting the animals from precipitation and wind are the main requirements for the design of rabbit cages..
Large rabbit farms house rodents in different types of cages in winter and summer. Winter cages are insulated with OSB or other fiber, and sometimes they are heated with water.
In regions with a temperate climate without extreme temperature fluctuations, rabbits can be kept year-round in identical portable cages, which are then moved indoors at the first frost. In the summer, these cages are moved outdoors again.
Selecting a location for installation
Rabbit hutches can be placed either indoors or outdoors. Outdoor hutches are recommended only in warm climates or in well-insulated, heated structures.
Rabbits don't tolerate high humidity well, so an outdoor location away from water, preferably at an elevated location, should be chosen. Direct sunlight can also be harmful to the rodents' health, so prospective rabbit breeders should provide a special shelter or hedge.
When placing rabbit cages indoors, the open part of the cage should be positioned toward the windows. This will increase daylight hours for the animals and provide them with more warmth. Daylight is very important for breeding, especially for young rabbits. Therefore, during the fall and winter, additional lamps will need to be installed to provide additional lighting and heat.
Don't forget about general hygiene in the areas where the animals are kept. Rabbits produce a lot of waste, which must be cleaned up promptly. A thorough cleaning of the entire structure and the area itself is recommended at least once a year. This will prevent the growth of bacteria and viruses.
Development
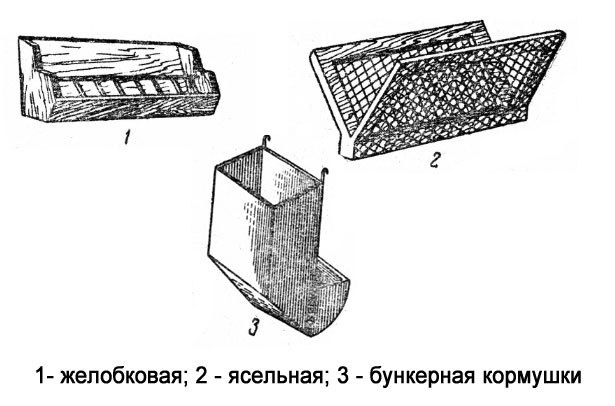
In addition to walls, floor and ceiling, housing for permanent keeping of rabbits provides a supply of fresh water and foodNowadays, you can buy ready-made waterers and feeders in stores or through specialized websites. However, simple feeders and waterers can be made at home.
Some rabbit hutch plans include built-in structures, while others require feeding equipment to be installed separately.
Flooring for pet rabbits should be soft to prevent the development of pododermatitis. Wood shavings or absorbent textile pads are considered the best options.
How to cage train a rabbit
In the wild, rabbits live in burrows. Providing them with adequate privacy is very challenging when keeping them productively. If a rabbit's cage is poorly designed, has sharp internal corners, is too small, or is located in a noisy area, the animals will experience stress, which will adversely affect their health and reproductive function.
Getting a rabbit used to a new home is quite simple: you just need to provide it with the most comfortable living conditions possible.
Rabbit breeding is a popular and profitable business in rural areas. The animals are kept in special cages, which can be built at home. Using the information and advice in this article, even the most inexperienced rabbit breeder can construct the perfect cage for their rabbits.