Even in our age of openness and frankness, there are topics that are uncomfortable to discuss. One such sensitive issue is pubic lice. Nevertheless, when faced with this problem, it is essential to address it promptly. To do this, it makes sense to take a closer look at some of the characteristics of the disease's progression and treatment.
Content
What is pubic lice?
Phthiriasis (pubic lice) is a parasitic sexually transmitted disease that affects hairy areas of the skin beneath which apocrine glands, which attract pubic lice with their odorous secretions, are located: the pubis, scrotum, perineum, armpits, and hair around the anus. In severe infestations, the parasites spread to eyelashes, eyebrows, mustaches, and sometimes even children's hair, but pubic lice never spread to the scalp of adults.
This is interesting. According to one scientific theory, the secretions produced by the apocrine glands contain pheromones, which are what make up a person's unique scent.
Both men and women suffer from phthiriasis. Contrary to popular belief, you cannot get pubic lice from animals.
Pathogen
The pubic louse (Crab louse) is a parasitic species of the suborder Lice that lives on the surface of the human body and feeds exclusively on human blood. Without food, the insect dies within 24 hours, but when removed from the body, it can remain viable for up to several months, entering a state of suspended animation.
This is interesting. Pubic lice can survive in water for up to two days, so the risk of contracting the parasite in a pool increases several times.
Description
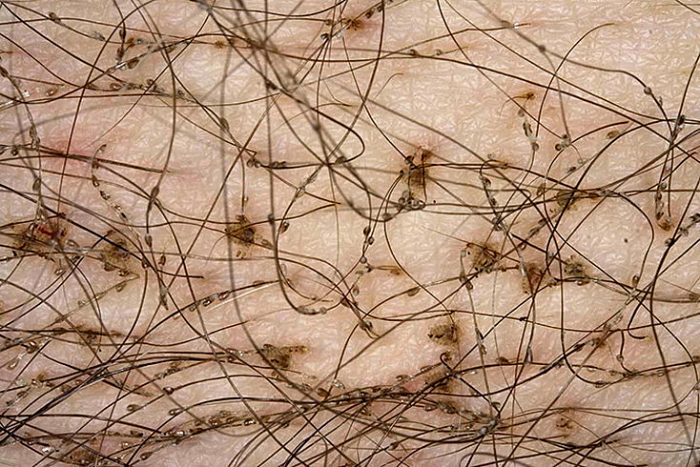
The crab louse is a light-brown insect with three pairs of large legs tipped with pincer-like appendages to help it cling to hair. They range in size from 1 to 3 mm, with females being almost 1.5 times larger than their male counterparts.
This is interesting. The pubic louse has massive legs, so when it spreads them out, the insect appears wider than it is long.
Reproduction and life cycle
Parasites lay eggs (nits) at the base of the hair shaft and attach themselves to the follicle openings. Because of the dense structure of pubic hair, they appear as little more than a small lump. The same can be said for nits: their microscopic size—just 0.5–0.6 mm long—and their round shape appear as a mere spot on the hair shaft. It takes 5–7 days for an egg to mature to the next stage of development, 13–17 days for the larva to become sexually mature, and just half a day for an adult louse to feed on blood, mate with a male, and lay its first egg. Over its 20–30 days of life, an adult louse can lay 30–50 eggs.
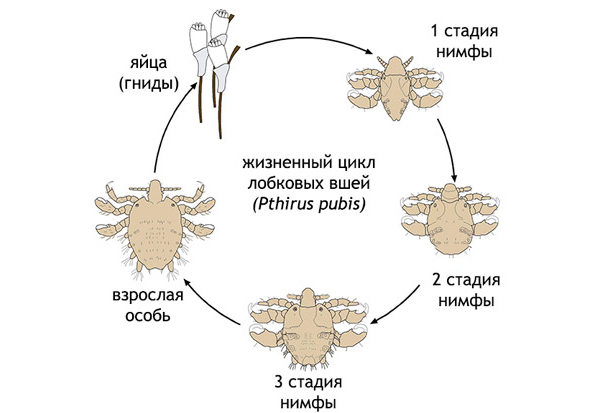
Over the course of 13–17 days, the larva, which is called a nymph due to its resemblance to the mature individual, goes through three stages of development with three molts.
Symptoms of phthiriasis
Pubic lice infestation is characterized by a rather long incubation period. In other words, once infected, a person may not know it for 14 to 30 days. At the end of this period, characteristic symptoms appear.
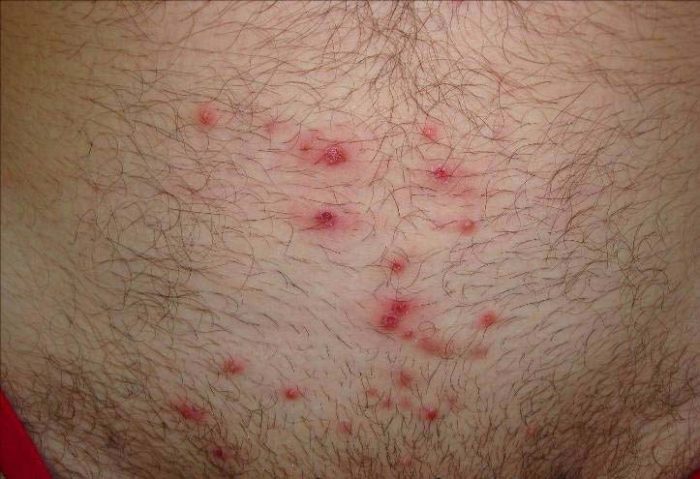
- Itching. Based on the definition of the disease, the pubic area is the most common site of itching. The intensity of the discomfort depends on the individual's sensitivity: some don't even notice it at first, while others can't stand it. The itching is especially intense during sleep. The affected areas are scratched, causing irritation and redness.
- Blue spots up to 1 mm in diameter. They are formed by a substance the louse releases during a bite to prevent blood clotting. The insect's saliva causes the breakdown of hemoglobin in human blood, and the breakdown products appear as blue dots under the skin.
- Allergic rash. This reaction is unique to each individual, meaning it's not universal. Blisters or papules may appear at the bite site, for example.
- The appearance of larvae on hair, lice on underwear, and skin. This symptom is characteristic of advanced stages of the disease.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of phthiriasis appear, consult a dermatovenerologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. Be prepared for the possibility that multiple diagnostic tests may be required, for example, if the infestation is not severe and lice are not visible to the naked eye, or if the insects have settled in hard-to-reach places, such as tangled, curly hair or skin folds.
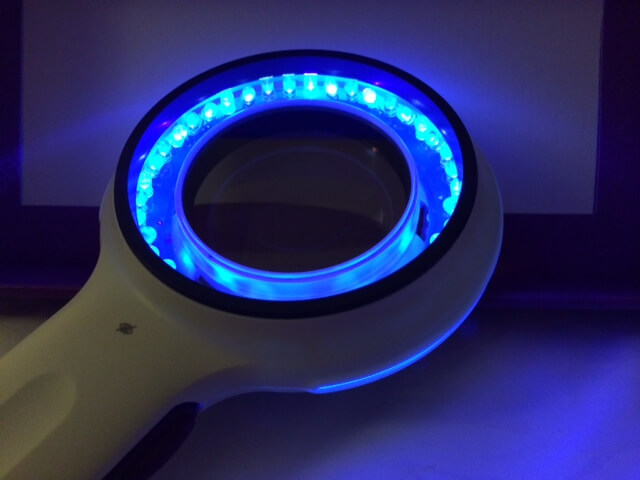
- Wood's lamp. Under the light of this device, live nits fluoresce white, while empty shells glow gray.
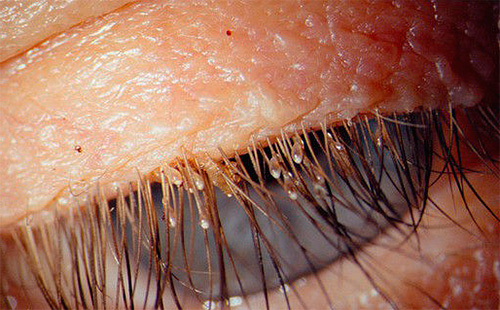
- A slit lamp used in ophthalmology can detect insects on eyelashes.
- Videodermatoscopy. A method that provides a 100% guarantee of an accurate diagnosis. A video camera polarizes light and, using a video capture device, transmits the captured image to a computer with 80x magnification, allowing for a clear view of not only lice but also their eggs.
Routes of infection
Until recently, pubic lice were thought to be a disease of those who don't monitor the number (or quality) of their sexual partners. However, the appearance of these unpleasant symptoms can be associated with a number of other factors:
- using a common towel;
- wearing someone else's clothes;
- sleeping in other people's beds;
- visits to the swimming pool, bathhouse, solarium, sauna;
- visits to public toilets.
This is interesting. In the last 10-15 years, when pubic shaving became fashionable, the incidence of phthiriasis has decreased significantly.
Possible complications
- Constant itching provokes scratching, which can cause allergic reactions and eczema.
- The risk of secondary infection in the scratched areas increases. First, pyoderma (pustules) appears, then, when the infection spreads to the lymph nodes and fatty tissue, boils and abscesses form. And if the body is weakened by other illnesses, all this can lead to blood poisoning.
- In 90% of cases, pubic lice is accompanied by other sexually transmitted diseases (most often syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia).
- When eyebrows and eyelashes become infected (especially in children), there is a risk of developing conjunctivitis and blepharitis - a recurring inflammation of the eyelash margin of the eyelids.
How to get rid of pubic lice
Phthiriasis was first described in the 17th century, so many methods of combating the parasite have been developed. They can be divided into three groups: mechanical, medicinal.s and folk. The first method will be the most radical and effective.
Mechanical method
If crabs have settled in the genital area, it is recommended to simply remove the hair, that is, shave it. In just about half an hour, the insects will have no chance to “catch on” to life.
This is interesting. Most representatives of this ancient profession remove pubic hair for preventative purposes: to avoid contracting lice from clients.
Medicinal method
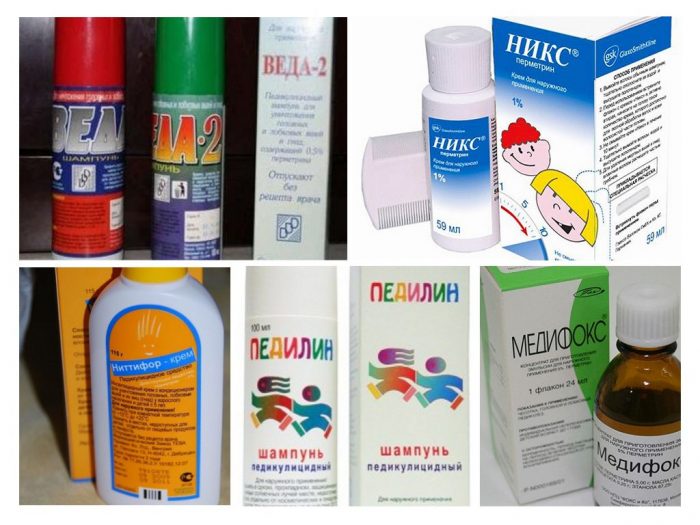
This involves treating the affected areas with insecticides that act as a nerve agent against insects but are safe for humans. Additionally, products containing dimethicone, a liquid silicone that clogs the insects' respiratory tract, can help combat pubic lice. As a rule, the lice removal procedure is carried out in two stages: first, the adult lice and larvae are destroyed, and then, during a repeat treatment (usually after a week), the nits and newly hatched larvae are destroyed. The choice of medication depends on the form in which it is available.
This is interesting. Along with treating your body, you should thoroughly treat your clothing and underwear. To do this, wash items at high temperatures (50 degrees Celsius or higher) and/or treat them with special chemicals, strictly following the instructions included with the product.
Table: Effective medications for combating pubic lice
| Release form | Name of the drug | Features of application | Notes |
| Emulsion | Medifox | 4 ml of 5% solution is added to 100 ml of water to obtain a 0.2% solution. The prepared emulsion is applied to the hair and washed off after 20 minutes (from 30 to 100 ml per treatment). | If the product is used in the form of a super-emulsion, then 0.5 ml of the solution is added to 50 ml of water to obtain a 0.1% emulsion, the prepared mixture is applied to the hair for 15–20 minutes, then washed off with warm water (from 30 to 100 ml per treatment). |
| Emulsion and shampoo | Pedilin | The emulsion is applied evenly to dry hair, rubbed in lightly and covered with a cotton napkin, and after 30 minutes, washed off with water, then shampoo is applied for 3 minutes and washed off, washing with shampoo is repeated 2 times (30 ml per treatment). | After the lice have been destroyed, shampoo is used periodically for preventative purposes. |
| Shampoo | Veda-2 | The shampoo is applied for 10 minutes, then washed off. After the procedure, all dead insects and larvae are removed from the hair. | |
| Soap | Vitar | The problem area is soaped for 20 minutes, then washed off with warm water. The treatment is repeated after a week (5–10 g per treatment). | |
| Cream | Nittifor | Apply the cream to the scalp, massaging it into the roots. After 10 minutes, rinse the treated areas with running water and regular soap or shampoo. | |
| Water-alcohol solution | The preparation is applied to the affected areas of the body and washed off after 40 minutes. A repeat preventative treatment is performed after a week. | ||
| Ointment | Benzyl benzoate | Apply to the problem area, after 3-4 hours the lice die, but the product has no effect on the eggs. | The main purpose of the ointment is to combat scabies. |
| Spray | Pax | The product is applied evenly to clean areas of the body. Its formulation allows it to reach even hard-to-reach areas. | Eliminates lice in one treatment. The treatment should be repeated after a week. |
| Lux | Destroys not only adults, but also larvae. | ||
| Nyuda | |||
| Pediculin | Designed for processing bed linen and underwear. | ||
This is interesting. If treatment is indicated for a child, it is essential to consult a pediatrician, who will help choose the best method for eliminating pubic lice.
Folk remedies
Since medications, despite their high effectiveness, contain insecticides that, while not directly dangerous to humans, are not recommended by manufacturers during pregnancy and lactation, home-based treatment is prescribed after consultation with a doctor.

Folk remedies for pubic lice can be divided into gentle, but not always effective, and aggressive ones, which can cause burns or other negative consequences.
Table: gentle remedies for the treatment of phthiriasis
This is interesting. Gentle folk remedies for treating phthiriasis are ineffective and require long-term use.
| Means | Features of application | Notes |
| Vinegar | Table vinegar is diluted with water (1:1), the affected areas are lubricated every day for 7-10 days, and washed off with warm water. | Under the influence of acid, lice and nits cannot stick to the skin and hair. |
| Cranberry juice | Squeeze out 2-3 handfuls of berries, mix with 1-2 teaspoons of honey and lubricate the infected areas 2-3 times a day. | |
| Mint and pomegranate juice | Add 3 tablespoons of mint to 1 cup of natural pomegranate juice, simmer for 8–10 minutes, and then rub into the affected areas 2–3 times a day. | Inconvenient due to frequency of use. |
| Geranium essential oil and castor oil | Mix 2 tablespoons of castor oil and geranium oil and rub into the affected areas twice a day. | The effectiveness depends on the degree of neglect: the more insects there are, the longer the treatment lasts (sometimes up to 2–3 weeks). |
Table: Use of aggressive folk remedies for phthiriasis
| Means | Features of application | Evaluation of effectiveness |
| 3% hydrogen peroxide | Dilute with water (1:1), apply to infected areas, and rinse with running water after 5–8 minutes. | Hydrogen peroxide cannot be used in its pure form, and when diluted, its effectiveness is significantly reduced. |
| 5% boric ointment | Rub into the affected areas, rinse after 4-5 minutes. Repeat once daily for three days. | The effect on nits is weak, so the procedure is repeated after a week. |
| 33% sulfur ointment | Apply to infected areas and wash off after 5–10 minutes. | It has a pungent odor. |
| Sulfur-mercury ointment | Toxic to humans | |
| Kerosene (technical or clarified) | Dilute with water (1:1), apply to dry skin with a cotton swab, rinse off after 5-10 minutes. | Burns to mucous membranes are possible. |
Video: Elena Malysheva's tips on how to get rid of pubic lice
Prevention
A disease like phthiriasis is easier to prevent than to treat. Moreover, preventative measures include generally accepted hygiene standards and ethical behavior.
- Wash regularly.
- Change and wash underwear daily.
- Don't wear other people's clothes.
- Try not to sleep in other people's beds.
- Avoid casual sexual contact with strangers.
- Iron things with a hot iron.
Despite the almost microscopic size of pubic lice, the problems they cause can be truly devastating. Itching, allergies, and infections can all be consequences of phthiriasis. Therefore, treatment should begin as soon as possible. However, before choosing a method to eliminate the parasites, it's essential to consult a dermatovenerologist who will provide an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the optimal treatment. As a rule, properly selected pubic lice treatments allow you to quickly get rid of the parasites, and following preventative measures will ensure you never have to worry about them again.