In many cultures around the world, cats are considered among the most mystical animals. This is, of course, primarily due to their glowing eyes. In ancient times, people could not explain this characteristic of cats and attributed all sorts of extraordinary properties to them.
However, in our time, now that scientists have clarified the origins of this phenomenon, these animals remain reverently regarded. Many still regard them as sacred, ascribed divine attributes to them.
Why do cats' eyes glow in the dark?
Unlike humans, cats have oval pupils, which, depending on the lighting, can narrow to slits or dilate to cover almost the entire iris. When comparing the structure of cats' eyes to humans, cats have significantly superior visual acuity. However, while the human eye can distinguish three spectra and seven colors, cats can only discern a greenish-blue tint.
Here are just a few of the features of our favorites:
The right and left eyes have their own visual fields that overlap. This explains cats' three-dimensional vision.
A cat's visual field is 285 degrees, while a human's is only 210.
The eyes distinguish shades of blue, blue, green, but they perceive red as gray.
The cat's eye notices the slightest movements.
Cats also lack the so-called “blind spot,” because their brain receives information from both eyes simultaneously.
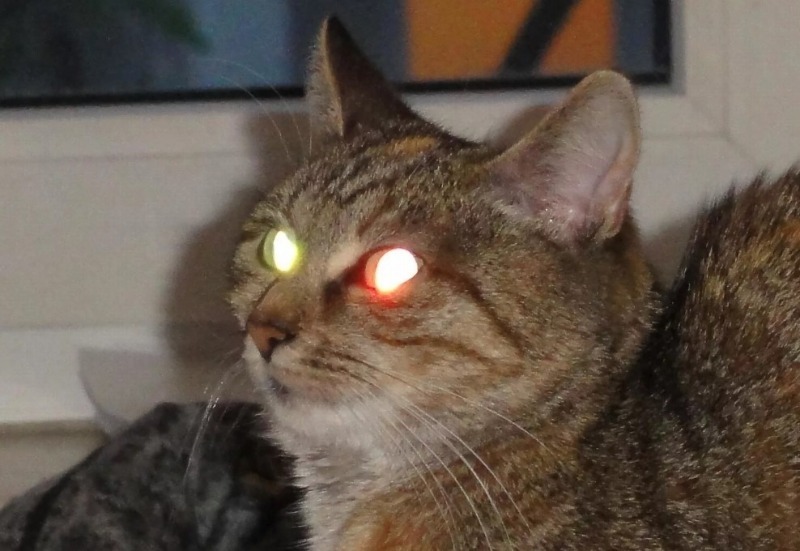
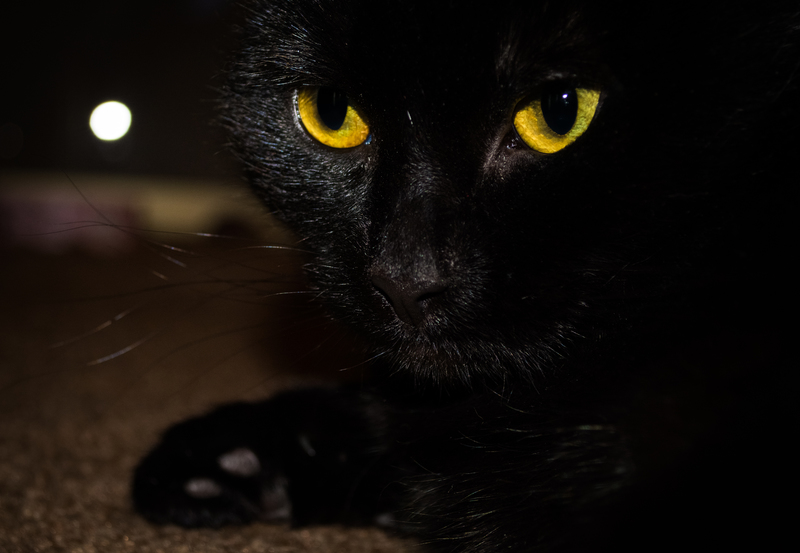
Cats' eyes do not glow in the dark, but rather reflect light, and the intensity of this phenomenon is determined by physiology.
The hidden part of the cat's eye is concave. In front of it is the crystalline lens, called the tapetum. It is the tapetum that allows cats to reflect light, which we perceive as luminescence.
Interestingly, the structure of the lens is similar in all cats, but the chemical composition varies. If the lens is pearlescent, it glows more brightly, while if the tissue is pigmented, the glow takes on a purple hue.
What color can a pet's eyes reflect?
Many have noticed that cats' eyes sparkle with different colors in the dark. This iridescent glow is caused by the tapetum lucidum and the pigments found within it.
Since the chemical composition of the lens varies in cats, the tapetum may not cover the entire fundus, but only a small portion. This is why the luminescence appears in various shades: yellow, violet, but most commonly, we observe green and yellow.
In rare cases, breed can also influence color. For example, Siamese cats typically have a crimson tint to their eyes.
Why do cats' eyes glow in the dark, while humans don't?
The structure of the human eye differs from that of a cat. The reflectivity of our retina is much weaker, but we too sometimes exhibit the ability to "shine our eyes." Just look at bad photographs and you'll see red pupils, which is very annoying for many people.
Our retina can only glow during a very brief and powerful flash. During a focused beam of light, our pupil reflexively constricts, blocking a large number of photons from entering the eye, which are then reflected by the retina. This is how our eyes begin to glow a "blood-red" color. But why red?
The thing is, the retina is designed in such a way that it's simply strewn with blood vessels. It's because of them that reflected light acquires its characteristic hue.
Cats are wonderful animals, and despite their wayward nature, they are dearly loved by many. They possess an amazing gift—the ability to share warmth and comfort with people. One can endlessly observe their grace and elegance, wondering: how do they do it? And of course, the answers will become much more interesting as we study their physiology.



1 comment