Content
Types of skin diseases in dogs - photos
Depending on the cause, skin diseases in dogs are divided into several types:
- allergic;
- parasitic;
- fungal;
- bacterial.
If an owner discovers skin lesions, they should take their dog to the vet without delay. However, despite the obvious symptoms and signs of the disease, an accurate diagnosis can be quite difficult, and treatment can be lengthy.
As soon as there is a suspicion that your pet has a skin disease, it is necessary to urgently take the following actions:
- Stop petting your pet.
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Do not allow the dog to sleep on the owner's bed.
- Avoid contact between your pet and children.
- To avoid spreading infection, stop brushing your dog's fur.
Avoid applying any ointments, brilliant green, or iodine to the affected areas before visiting the doctor. You can trim the fur and treat the skin with salicylic alcohol.
Fungal skin diseases
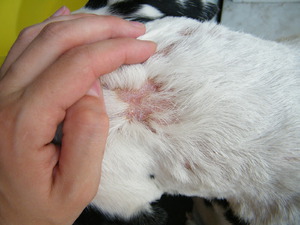
Dermatophytosis is easily transmitted from animal to animal via fungal spores. Yorkshire Terriers are particularly susceptible.
Symptoms of fungal skin diseases:
- Alopecia that is rarely itchy and never has associated lesions.
- Lesion of the elbow joint and nail, which exfoliates and turns yellow.
- Rarely - nodular skin lesions that may release pus.
- In severe forms of the disease, the paw pads may be affected by microspores.
For fungal infections, veterinarians most often prescribe treatment with specialized shampoos, including Dermazole and Nizoral. A special medication for animals, Imaverol, is also used. A course of treatment with specialized antifungal medications, such as Terbinafine, Itraconazole, and Ketoconazole, is also prescribed.
A specialist must advise the owner of a sick dog that in order to destroy fungal spores, it is necessary to treat the pet's bedding and wash all its habitats.
Allergies in dogs
Identifying the allergen is not very easy, so allergic skin diseases are quite difficult to diagnose. The most common dog allergens are:
- food products;
- house dust;
- insect bites;
- plant pollen;
- mold;
- household chemicals;
- medicinal preparations.
A fairly common allergen is commonly used flea control products. Even the most harmless ones belong to the pyrethroid group and therefore often cause allergic reactions.
To the main ones symptoms of the occurrence of allergies in dogs refers to:
- severe itching;
- salivation;
- runny nose;
- sudden cough;
- urticaria;
- edema.
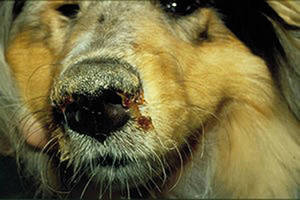
A rapidly developing allergic reaction is the easiest to detect. A thorough investigation can quickly identify and eliminate the cause of the allergy. Most often, such reactions are characterized by the sudden onset of a runny nose, cough, and hives, which manifest themselves as itchy blisters on the face, under the arms, and in the groin. Hives disappear fairly quickly, but to prevent the pet from scratching the blisters and causing an infection, the inflamed areas of skin are wiped with vodka or salicylic alcohol. Additionally, the dog should be given suprastin, tavegil, or diphenhydramine three times a day.
The causes and sources of delayed allergic reactions are identified in stages:
- First of all, you should rule out the presence of parasites in your pet.
- After this, an elimination diet is prescribed, which lasts for two to three months.
- If the dog is parasite-free and eats all foods without any reaction, then an environmental allergy is diagnosed. Specific allergy tests can determine the pet's reaction.
Food allergies in dogs are uncommon, but if your pet has an allergic reaction to certain foods, they should be eliminated from the diet.
Mostly Allergy treatment is carried out according to the following scheme:
- taking medications that relieve itching;
- infection control;
- regular treatment against parasites that aggravate the symptoms of the disease.
Parasitic skin diseases

Symptoms of parasitic diseases include:
- Ear damage and accumulation of wax in them due to otodectosis.
- Severe itching in the neck, head, and paws is associated with sarcoptic mange. The dog scratches the wounds to such an extent that the skin becomes inflamed and the fur is removed.
Treatment for parasitic diseases involves treating the animal with Frontline or Advantix, both antiparasitic medications. These should be applied to the pet's withers twice daily for a month.
Scabies or aranchnosis
This is another parasitic skin disease caused by small mites. The parasites live in the skin, sebaceous or sweat glands, hair follicles, or the parenchyma of the animal's internal organs. The mites are so small that they cannot be detected without a magnifying glass. They can come in various forms, and depending on this, dogs There are different types of scabies:
- Railwaywoman.
- Ear mites.
- Scabies.
Some forms of these diseases are contagious to humans, but are quickly cured without the use of any drugs.
A symptom of scabies is localized itching, most often found in the ears, hocks, and elbows. Over time, the mites not only infect the surface of the skin but also begin to irritate the nerve endings, causing the itching to become unbearable. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion of scabies, it must be treated immediately. Otherwise, the pet may experience metabolic disorders and become malnourished. In severe cases, if left untreated, scabies the animal may die.
Treatment for the disease must be comprehensive. First and foremost, the itching must be soothed and the mites destroyed. At the same time, it is necessary to improve skin regeneration and boost the immune system. Some dogs do not fully recover, and as soon as their immune system weakens, their hormonal status changes, or the pet becomes stressed, the disease can recur.
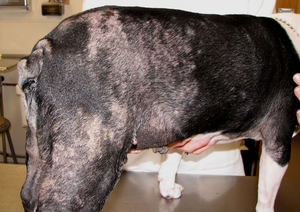
Seborrhea
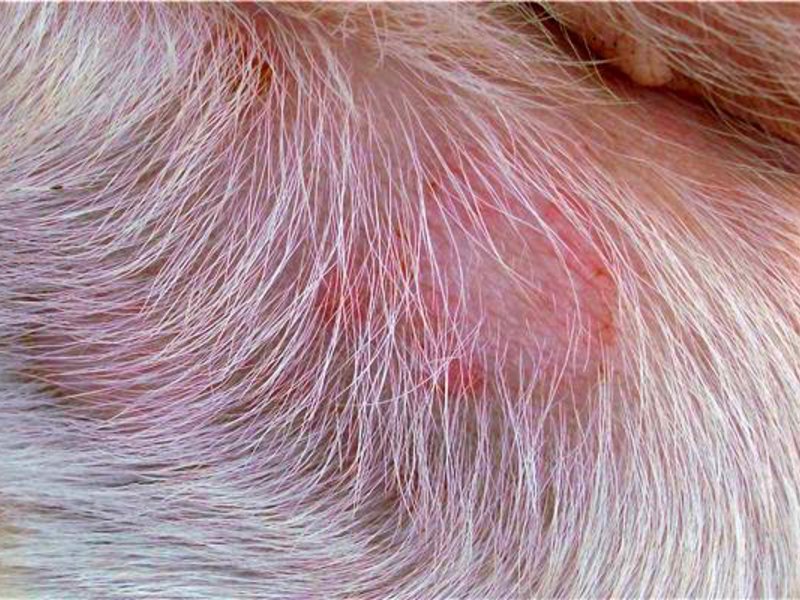
The first outbreaks of the disease appear on the lower abdomen and on the pawsThen the dandruff spreads to the ears and tail, hocks and elbows, muzzle and chest.
There are two types of seborrhea:
- Dry. This type is characterized by dry skin, which is covered with flaky, dry, and flaky dandruff.
- Oily. This condition is characterized by excess sebum, greasy flakes sticking to the fur, brown plaques on the skin, and a rancid odor.
Dry seborrhea most often affects small lap dogs, who are frequently bathed with various detergents. This results in dehydrated skin and dry dandruff.
In some cases, dry seborrhea can be caused by a lack of fat in the animal's diet. To get rid of dandruff, you can try adding a teaspoon or dessert spoon of vegetable oil to your dog's diet daily. If the dandruff persists after some time and the itching intensifies, consult a specialist.
As soon as the tests show that seborrhea is not associated with parasites and fungi, you can begin to treat it. treatment with antiseborrheic agentsTo do this, treat the affected areas with a special shampoo once or twice a week, leave it on the skin for 10 minutes, and then rinse. Afterward, massage Pragmatar ointment or Thiomar cream into thoroughly dry skin. It's recommended to hold your pet until the cream or ointment is fully absorbed to prevent them from licking it off.
Since in some cases seborrhea is a consequence of some disease, the doctor prescribes medications to treat the underlying disease.
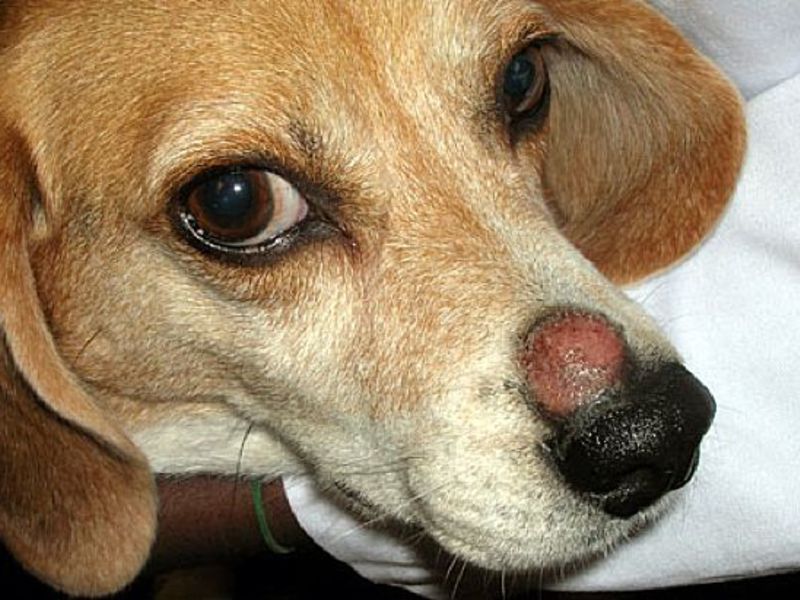
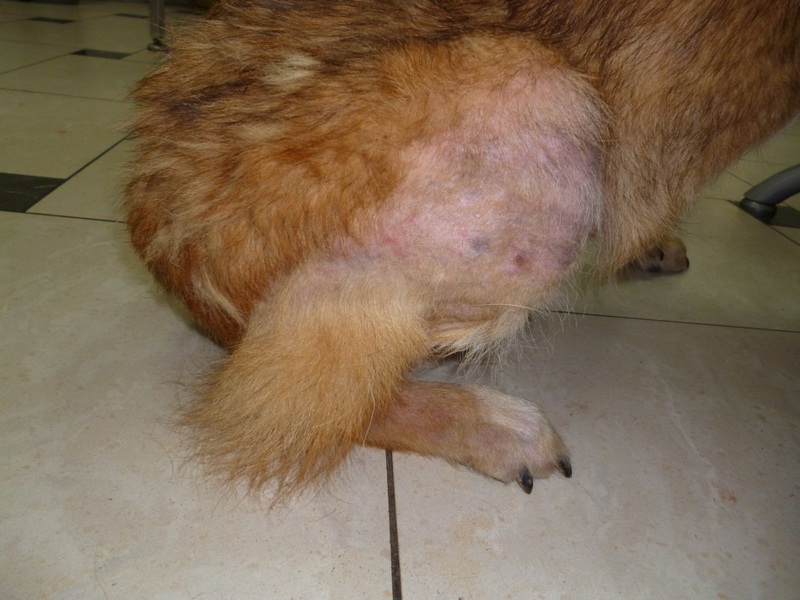
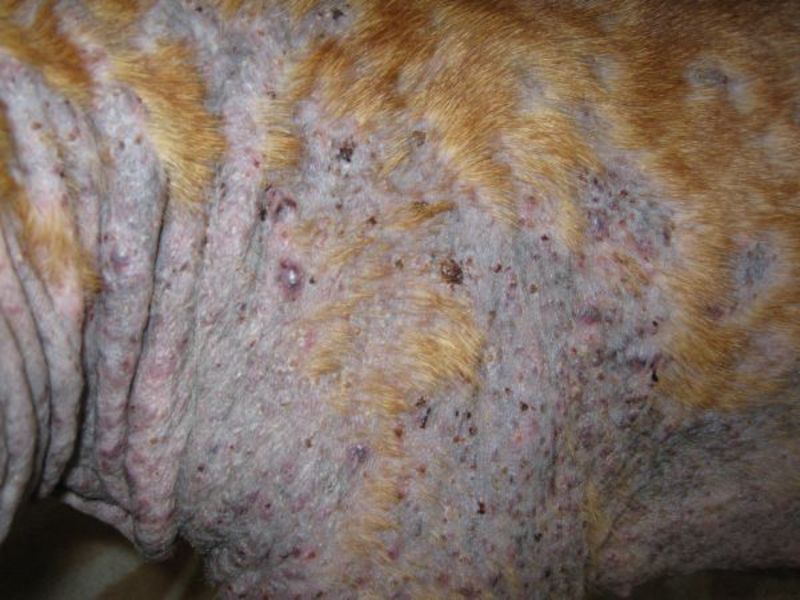
Dermatitis in dogs
Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin. The causes of this condition can be very diverse. According to them, all dermatitis in dogs have a conditional qualification:
Traumatic. The disease occurs as a result of exposure to a negative factor on the skin.
- Allergic.
- Inflammatory. May occur with inflammation of skin folds in Chow Chows, Bulldogs, and Mastiffs.
In some cases, the disease is associated with age. In pets in their first years of life, dermatitis manifests as purulent and purple blisters and pustules on the lips, chin, groin, and hairless abdomen. In older dogs, the disease manifests itself in the area of the knee joints and along the back, where papules, pustules, or an acne-like rash are found.
With any dermatitis, painful areas are treated with antibacterial soap and 3% hydrogen peroxide. If this doesn't help, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
To treat your pet, it needs a proper diagnosis, which can only be done in a clinic. Specialists will examine your pet, run the necessary tests, and prescribe appropriate treatment based on these tests. It's important to remember that treating skin conditions in dogs on your own is virtually impossible. Don't delay a visit to the veterinarian, as wasted time can lead to suffering and, in some cases, death.

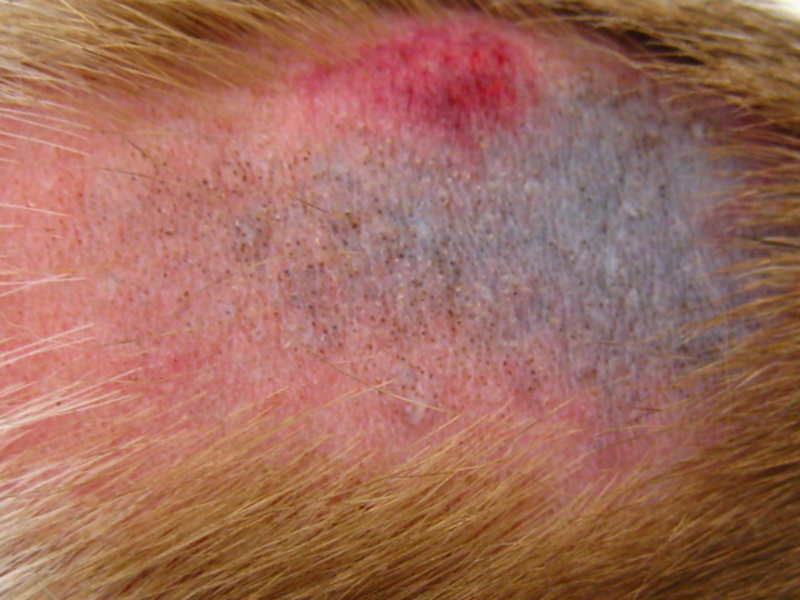

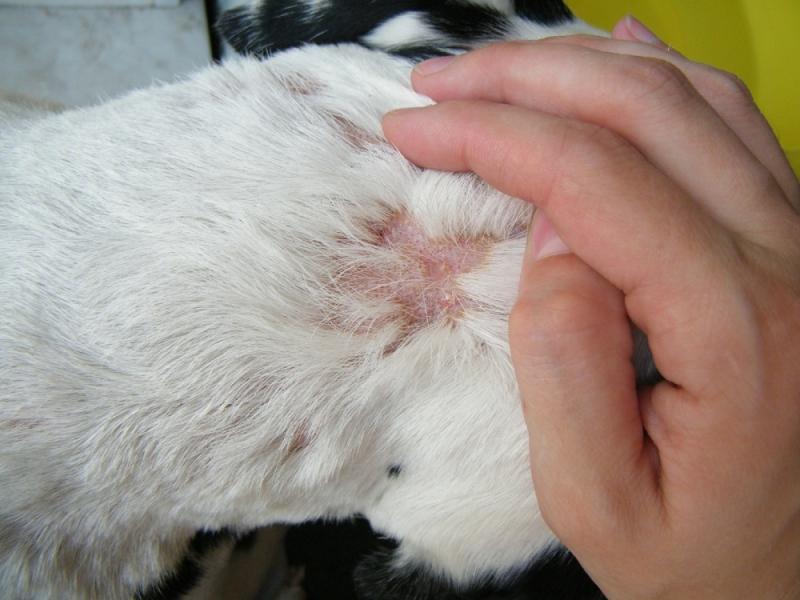
 Traumatic. The disease occurs as a result of exposure to a negative factor on the skin.
Traumatic. The disease occurs as a result of exposure to a negative factor on the skin.